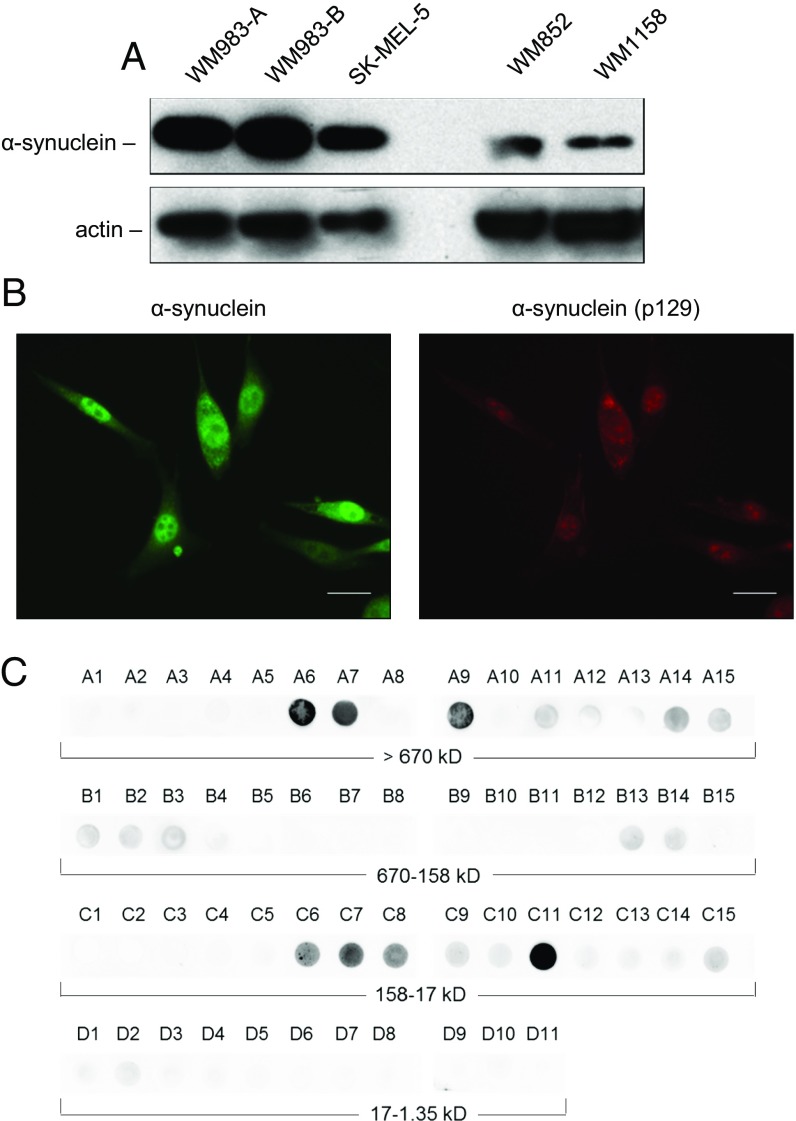
Fig. 2.
Expression and presence of monomeric as well as oligomeric species of α-synuclein protein in melanoma cells. (A) Immunoblot analysis of α-synuclein expression in the VGP melanoma cell line WM983-A; in the MGP melanoma cell lines WM983-B, SK-MEL-5, and WM852; and in the RGP/VGP melanoma cell line WM1158. Ten micrograms each of whole-cell lysate, prepared from WM983-A, WM983-B, or SK-MEL-5 cells, was loaded per lane. To visualize clearly expression of α-synuclein protein in the low-level α-synuclein–expressing melanoma cell lines WM852 and WM1158, 20 µg each of whole-cell lysate was loaded per lane. Probing with an anti-actin antibody served as loading control. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of α-synuclein expression in WM983-B melanoma cells probed with antibody to α-synuclein (pseudocolored green) or phosphorylated α-synuclein (pSer129) (pseudocolored red). (Scale bars, 30 μm.) (C) Presence of monomeric as well as α-synuclein oligomeric species in WM983-B melanoma cells detected by SEC–filter trap assay. Collected fractions (A1 > A15, B1 > B15, C1 > C15, D1 > D11) were applied to nitrocellulose membrane and probed with an anti–α-synuclein antibody.