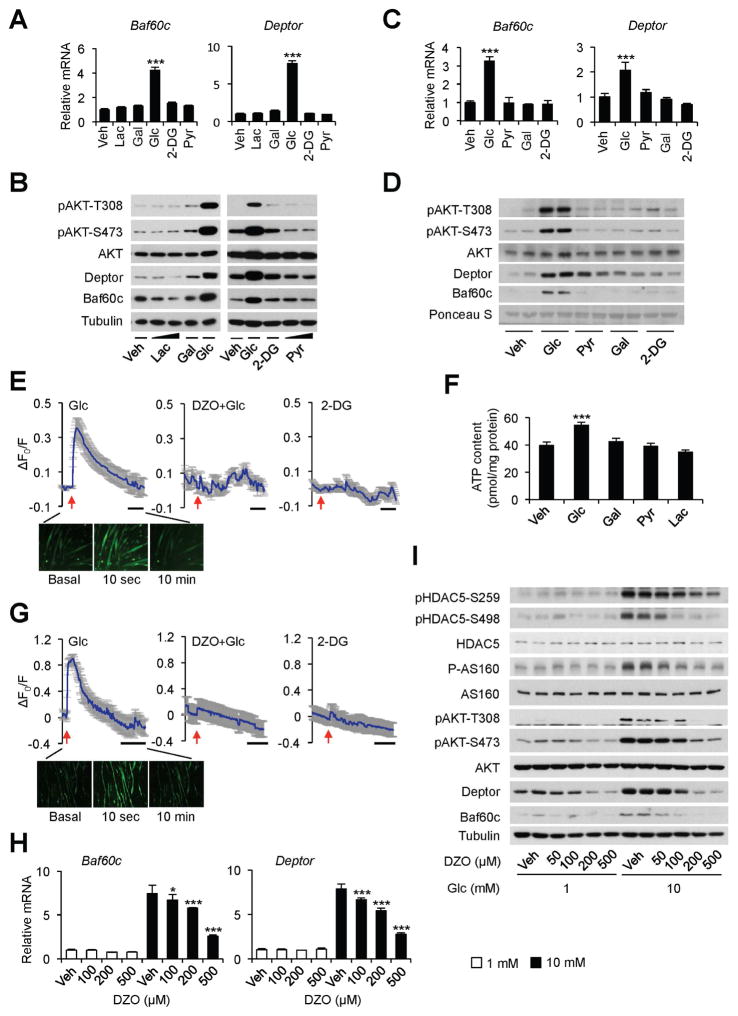
Figure 3. Glucose elevates intramyocellular calcium levels through a KATP channel-dependent pathway.
(A) qPCR analysis of gene expression in C2C12 myotubes treated with vehicle (Veh) alone or 10 mM of indicated treatments for 12 h. Lac, lactate; Gal, galactose; 2-DG, 2-deoxyglucose; Pyr, pyruvate. Data represent mean ± SD. ***p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA.
(B) Immunoblots of total cell lysates from C2C12 myotubes as treated in (A).
(C) qPCR analysis of gene expression in ex vivo cultured EDL muscles with indicated treatments for 4 h. Data represent mean ± SEM (n=3). ***p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA.
(D) Immunoblots of total protein lysates from ex vivo cultured plantaris muscle as treated in (C).
(E) Top, calcium imaging traces in C2C12 myotubes in response to 10 mM glucose (left), 100 μM diazoxide (DZO) pretreatment followed by 10 mM glucose treatment (middle), or 10 mM 2-DG (right). Data represent mean ± SD. Bottom, representative fluorescent images in C2C12 myotubes treated with 10 mM glucose.
(F) ATP content in treated C2C12 myotubes. Data represent mean ± SD. ***p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA.
(G) Top, calcium imaging traces in primary mouse myotubes in response to 10 mM glucose (left), 100 μM diazoxide (DZO) pretreatment followed by 10 mM glucose treatment (middle), or 10 mM 2-DG (right). Data represent mean ± SD. Bottom, representative fluorescent images in primary mouse myotubes treated 10 mM with glucose.
(H) qPCR analysis of Baf60c and Deptor expression in C2C12 myotubes treated with 1 or 10 mM glucose in combination with Veh or DZO for 12 h. Data represent mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001; two-way ANOVA.
(I) Immunoblots of total lysates from C2C12 myotubes treated as in (H).
See also Figure S2 and S3.