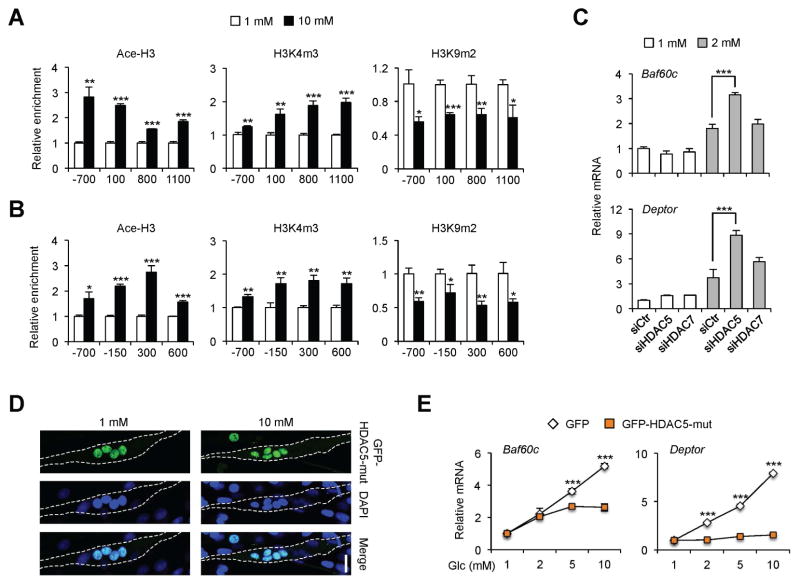
Figure 5. HDAC5 mediates the induction of glucose-responsive genes in cultured myotubes.
(A, B) ChIP assay in C2C12 myotubes treated with 1 mM (open) or 10 mM (filled) glucose using antibodies against Acetyl-Histone 3 (Ace-H3), trimethyl-H3K4 (H3K4m3) or dimethyl-H3K9 (H3K9m2). The locations of the qPCR primers relative to the transcription start site of Baf60c (A) and Deptor (B) are indicated. Data represent mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test.
(C) qPCR analysis of gene expression in transduced C2C12 myotubes. Data represent mean ± SD. ***p < 0.001, two-way ANOVA.
(D) Immunofluorescence images of GFP-HDAC5-Mut and nuclei (DAPI) in C2C12 myotubes transduced with an adenovirus expressing GFP-HDAC5-Mut, and treated with 1 mM (top) or 10 mM (bottom) glucose. Scale bar: 25 μm.
(E) qPCR analysis of gene expression in C2C12 myotubes transduced with GFP or GFP-HDAC5-mut adenoviruses. Data represent mean ± SD. ***p < 0.001, two-way ANOVA.
See also Figure S5.