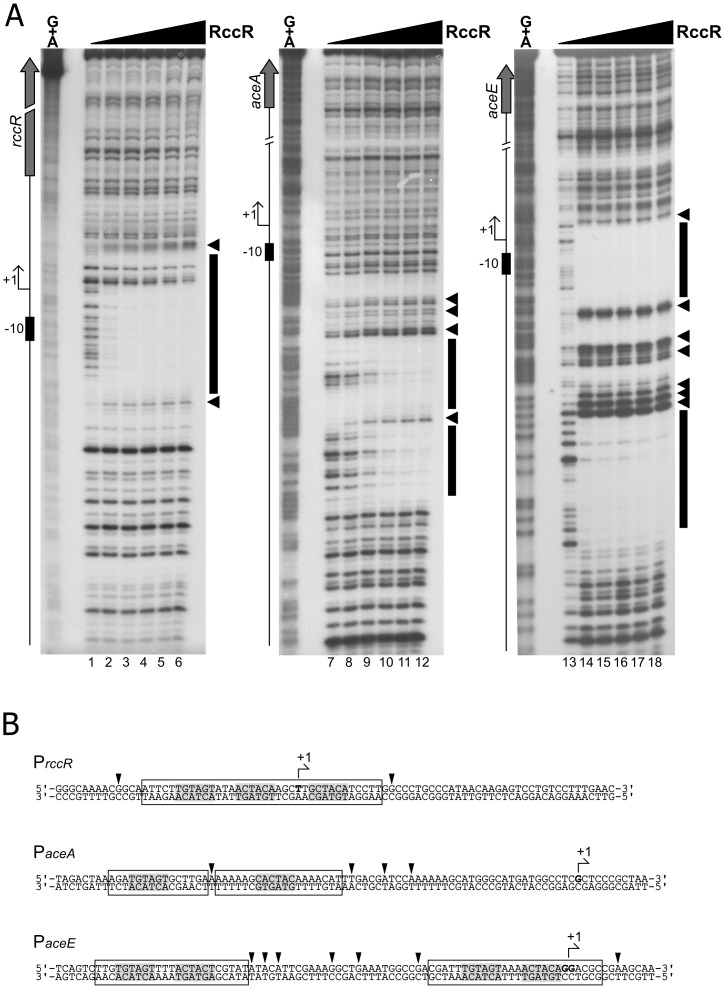
Fig 8. RccR binds the 28bp and the 15bp binding sites.
8A: DNaseI footprinting panel of RccR on rccR, aceA, aceE promoters. Radiolabelled promoter probes were incubated with increasing concentrations of purified RccR-His (0, 10, 20, 40, 80, 160 nM of RccR-His from left to right in each panel) before DNaseI digestion and DNA purification. Recovered DNA fragments were subjected to electrophoretic separation along with a Maxam and Gilbert G+A sequence reaction ladder (leftmost lane of each autoradiograph). On the left of each autoradiograph, a schematic representation of the genomic region is reported, with symbols as follows: block arrow represents the coding sequence, bent arrow represents the transcriptional start site identified in this study (S3 Fig), while black box indicates the -10 promoter element. Protected regions are highlighted by a black box on the right of each autoradiograph, while DNaseI hypersensitive sites are evidenced by black arrowheads. 8B: mapping of the RccR binding sites on the rccR, aceA and aceE promoter regions. Arrowheads denote hypersensitive sites, protected regions are included in open boxes, and conserved pseudopalindromic sequences are highlighted in light grey. Bent arrow indicates the transcriptional start site identified in this study (S3 Fig) and the first transcribed nucleotide is in bold.