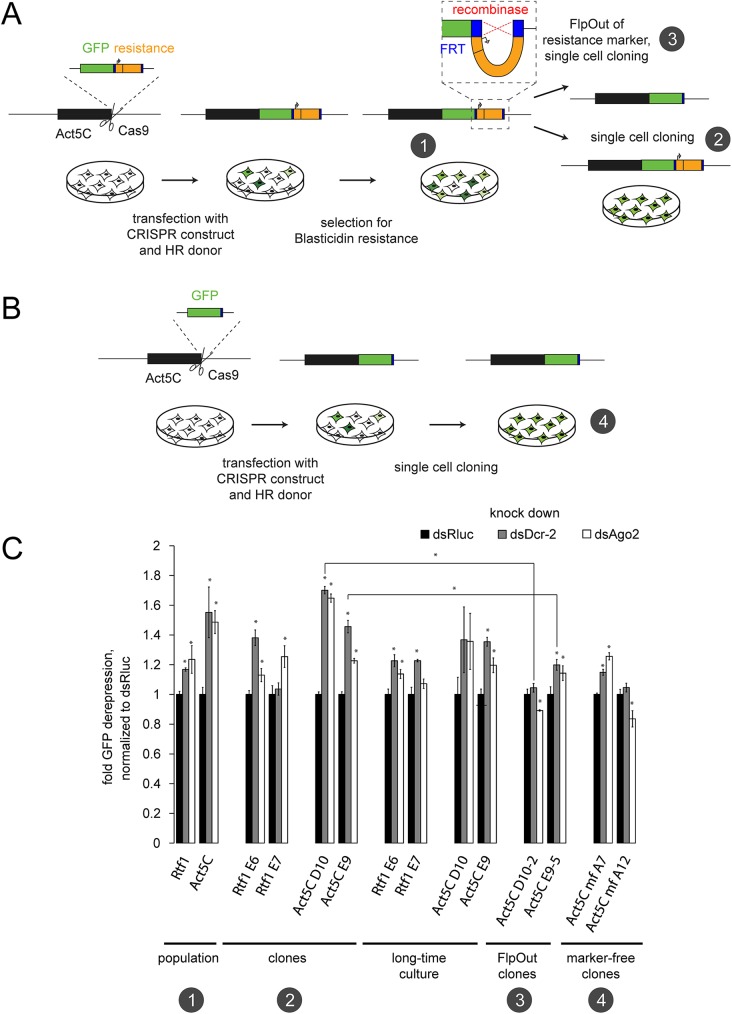
Fig 1. GFP-based reporter assay can detect siRNA mediated repression after genome engineering.
(A) PCR-based tagging workflow using CRISPR/Cas9 in Drosophila Schneider cells. After introducing a DSB at the act5C locus by the Cas9 enzyme, the HR donor (consisting of homology regions, the GFP coding sequence and the resistance cassette) integrates and GFP-positive cells can be eriched by drug selection (number 1) and cloned (number 2). The recombinase mediates the FlpOut of the resistance cassette and subsequent single cell cloning results in FlpOut clones (number 3). (B) Marker-free tagging of the act5C locus with GFP. Similar to (A), the act5C locus can be tagged without an selection marker. Single cell cloning resulted in homogeneous cell lines (number 4). (C) GFP-based reporter assay detecting the presence of functional siRNAs in several cell lines. Knockdown of Dcr-2 and Ago2 as key players of the RNAi pathway leads to derepression of the GFP fluoresence in the twoAct5C-GFP and Rtf1-GFP cell lines. Fluorescence levels (FL1 channel) were normalized to control knockdown (Rluc). Error bars represent standard deviation (n = 3). Significant differences were calculated though an unpaired t-test (unequal variance) on the data (* p < 0.05).