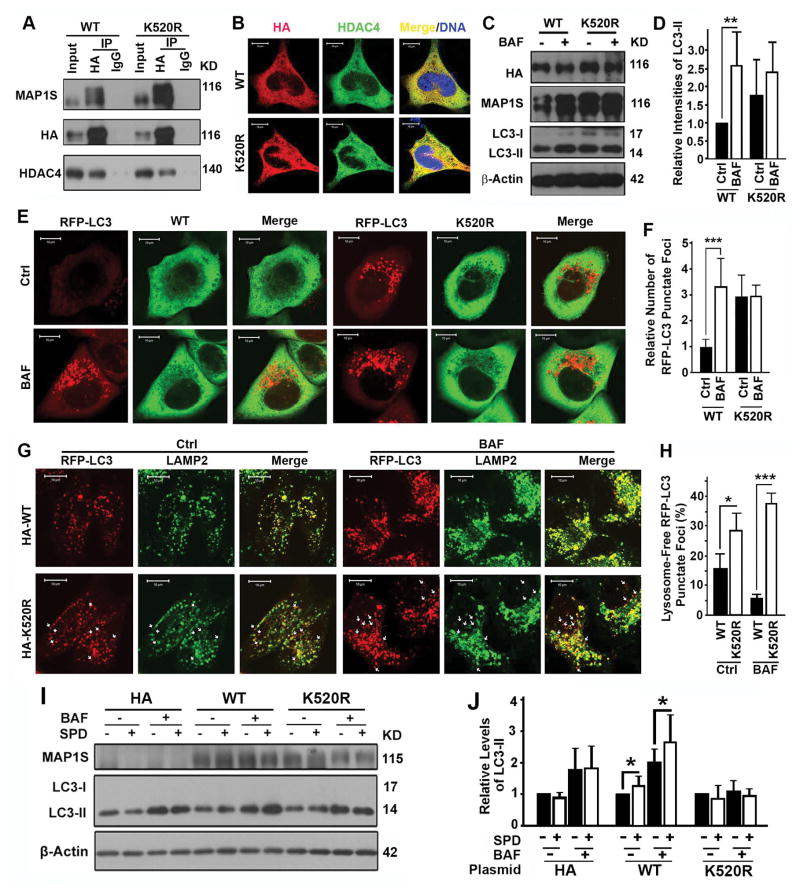
Figure 7.
Lysine 520 of MAP1S is important for MAP1S to promote autophagosomal degradation. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation analyses of the interaction of HDAC4 with wild-type (WT) or K520R mutant MAP1S in 293T cells transiently expressing wild-type or K520R mutant MAP1S. (B) Analyses of the colocalization of HDAC4 with wild-type and K520R mutant MAP1S. (C–F) Analyses of the impact of K520R mutation on autophagy flux. Representative immunoblots of LC3-II in HeLa cells (C) and fluorescent microscopic images of RFP-LC3 punctate foci in HeLa cells stably expressing RFP-LC3 (E) and their respective quantification (D,F) are shown. (G,H) Analyses of the impact of K520R mutation on the colocalization of RFP-LC3 punctate foci with lysosomes stained with anti-LAMP2 antibody. Representative images (G) show lysosome-associated (yellow in merge) and lysosome-free RFP-LC3 punctate foci (red spots, some are pointed out using white arrows). Quantification (H) shows the percentages of lysosome-free to total RFP-LC3 punctate foci. (I,J) Analyses of the impact of K520R mutation on the ability for MAP1S to restore the impact of spermidine on autophagy flux in MAP1S−/− MEFs. Representative immunoblots (I) and quantification (J) are shown.