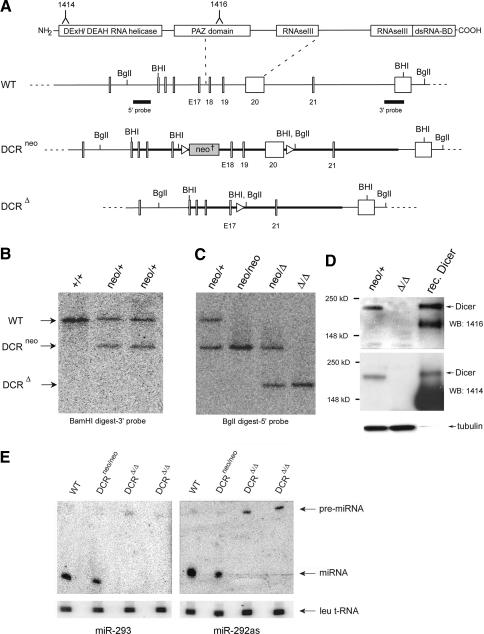
Figure 1.
Conditional gene targeting of mouse dcr-1. (A) Depicted at the top is the structure of the Dicer protein composed of an N-terminal RNA helicase domain, PAZ domain, followed by two catalytic ribonuclease III domains and a double-stranded RNA-binding domain. Epitopes used for generation of anti-Dicer antibodies are indicated. Below it, part of the wild-type (WT) dcr-1 gene is depicted. Exons 18–20, encoding half of the PAZ domain and the first RNase III domain, are flanked by loxP sites (triangles). The locations of BamHI (BHI) and BglI restriction sites and 5′ and 3′ probes used for screening of homologous recombinants are indicated. Homologous recombination of our targeting vector (bold line) resulted in the allele depicted as DCRneo. An FRT-flanked PGK-neomycin cassette (neo†) is inserted into intron 17. Upon Cre-mediated recombination of the introduced loxP sites, a Dcr-null allele is generated (depicted as DCRΔ). (B) Southern blot of BamHI-digested genomic DNA from a wild-type (+/+) ES cell clone, and two homologous recombinants (neo/+) were hybridized with the 3′ probe (see A). (C) Southern blot of BglI-digested genomic DNA from a heterozygous (neo/+) ES cell clone, a homozygous (neo/neo) clone, a heterozygous deleted clone (neo/Δ), and a homozygous (Δ/Δ) Dcr-null clone was hybridized with the 5′ probe (see A). (D) Western blot of extracts derived from a heterozygous (neo/+) ES cell clone, a homozygous (Δ/Δ) clone, and recombinant Dicer (rec. Dicer) protein. The Western blot was probed for Dicer protein using antisera raised against two different peptides homologous to mouse Dicer (the corresponding epitopes, 1414 and 1416, are indicated on the schematic representation of Dicer protein, A), and then stripped and reprobed for tubulin (bottom). (E) Northern analysis of miRNA expression in mouse ES cells. Total RNA from a control wild-type and Dicer-proficient clone (neo/neo) and two Dcr-null clones (Δ/Δ) was resolved in a denaturing polyacrylamide gel and transferred onto a nylon membrane. Shown are PhosphorImages of two blots hybridized either to a radiolabeled oligonucleotide complementary to miR-293 (left panel) or miR-292as (right panel). To control for equal RNA loading, the Northern blots were also reprobed for leucine transfer RNA (Leu tRNA). The arrows indicate Leu tRNA, pre-miRNA, and processed mature miRNA.