Figure 2.
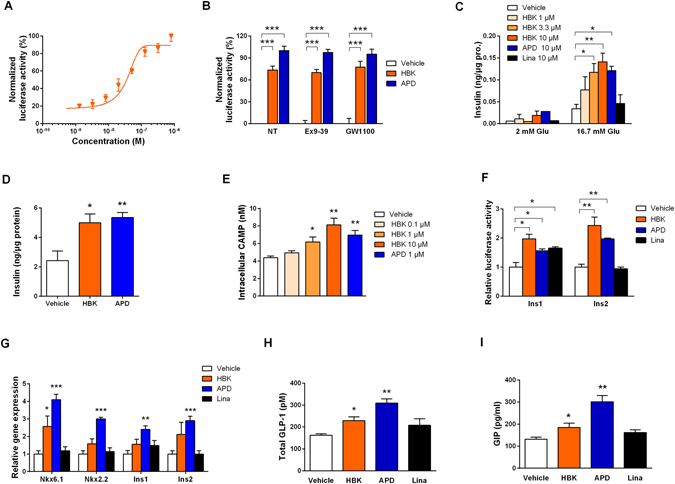
HBK001 activates GPR119 and induces insulin secretion ex vivo and incretins release in vivo. (A,B) HBK001 exhibits GPR119 activation efficacy in HEK293 cells. HEK293 cells were transiently co-transfected with Peak13-CD5L-hGPR119, pcDNA3.1-Gal4-CREB and Peak12-Gal4UAS-luci plasmids, and then treated with HBK001 at indicated concentrations for 24 hours and luciferase expression in cell lysates was measured by chemiluminescence. (A) Concentration-dependent activity of HBK001 on GPR119 transactivation; (B) Activation potency of HBK001 (10 μM) on GPR119. Data were normalized to the positive control, APD597 (Maximum activity was set as 100%). At the same time, the compounds were added with antagonists of GLP1R and GPR40, Ex9-39 and GW1100, respectively, or without these antagonists (NT) to identify whether inhibition of GLP1R or GPR40 influences the transactivation of GPR119 by the compounds. The concentration of Ex9-39 and GW1100 was 1 μM and 10 μM, respectively. (C) Insulin secretion in isolated primary islets from ICR mice in the presence of glucose (2 mM or 16.7 mM) and different compounds as indicated. The concentration of insulin was quantified by ELISA and was expressed as a ratio to the concentration of total protein in islets. (D) Insulin secretion in isolated primary islets from a human donor in the presence of 16.7 mM glucose and different compounds as indicated. The concentration of insulin was quantified by ELISA and was expressed as a ratio to the concentration of total protein in islets. (E) Intracellular cAMP production in mouse NIT-1 cells after treatment of compounds at the concentration of 10 μM. (F) Determination of HBK001 on transactivation of mouse insulin gene 1 and 2 (Ins1/2) in HEK293 cells co-transfected with Peak13-CD5L-hGPR119, Peak12-Ins1/2-luci and pRL-TK. (G) The effect of HBK001 on gene expression correlated with insulin secretion was explored using real-time PCR assay in mouse primary islets after 24 hours of compound treatment. In all of above experiments, solvent DMSO was used as vehicle control, HBK001 and linagliptin was treated at the concentration of 10 μM or as specifically indicated in the figure. (H,I) Serum total GLP-1 (H) and GIP (I) levels at 10 min after the glucose loading in 4 h-fasted ICR mice administered with vehicle (distilled water), HBK001 (30 mg/kg), APD597 (20 mg/kg) and linagliptin (2 mg/kg) by gavage 1 hour prior to oral glucose load (2 g/kg). Data are presented as mean ± SEM (A to G, n = 3; H, I CTGCAAAGGTTTGTCCC, n = 10), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus Vehicle.
