Figure 4.
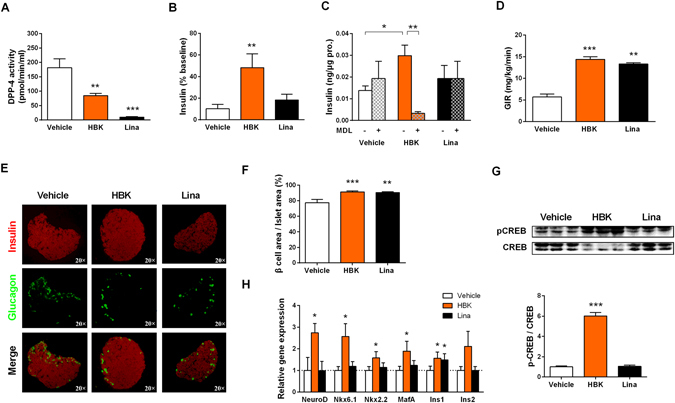
HBK001 promoted insulin secretion and improved islet β-cell function in KKAy mice via a GPR119-dependent pathway. (A) Blood DPP4 activity measurements on the 48th day of HBK001 treatment. (B) HBK001 treatment increased first-phase insulin secretion in the hyperglycemic clamp test. Insulin secretion levels were measured 5 min after glucose infusion. (C) Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) determination in primary islets of KKAy mice. Primary islets isolated from KKAy mice in the presence of 16.7 mM glucose and 10 μM HBK001 or linagliptin while DMSO was used as a vehicle control. At the same time, the adenylyl cyclase inhibitor, MDL12330A (MDL), was added to block production of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). (D) HBK001 treatment increased the glucose infusion rate (GIR) in the hyperglycemic clamp test. (E) HBK001 treatment normalized islet morphology and increased β-cell area in the pancreas of spontaneous type 2 diabetic KKAy mice. Immunostaining of insulin (red) and glucagon (green) in pancreatic sections. (F) β-cell percentage of total islet area. (G) Western blot analysis of CREB protein phosphorylation in pancreas of KKAy mice treated with HBK001 and linagliptin. (H) Quantitative PCR analysis of genes related to β-cell function and survival in KKAy mice treated with HBK001. A comparative cycle threshold (CT) method was used for relative quantification of gene expression between different groups; β-actin was used for normalization. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (A, n = 10; B,D–F,H, n = 5; C,G, n = 3), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus Vehicle.
