Fig. 4.
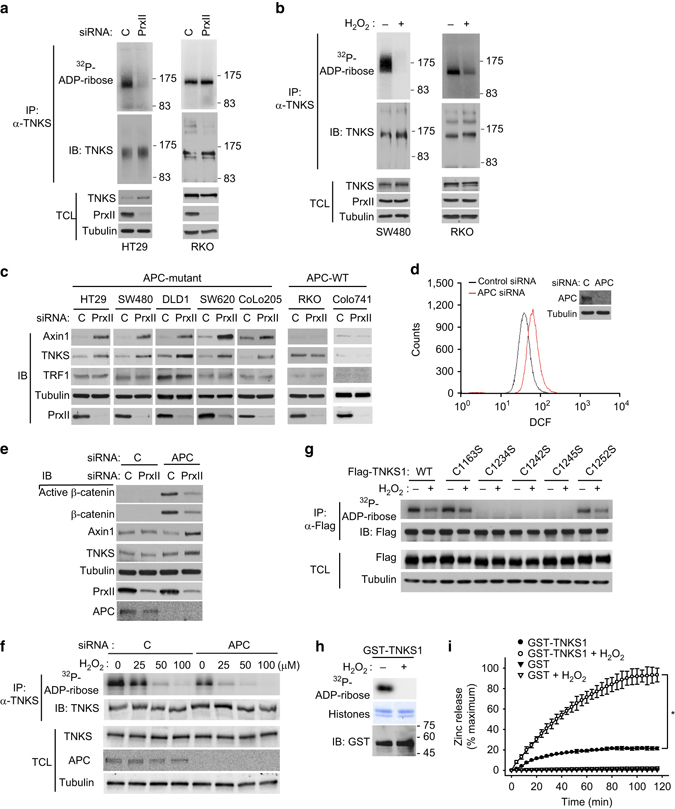
PrxII is required for PARP activity of TNKS that is sensitive to oxidative inactivation by H2O2. a HT29 and RKO cells were transfected with control or PrxII-1 siRNA and lysed for immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-TNKS antibody. The immunoprecipitated TNKS was subjected to in vitro PARP assay as described in the Methods. Total cell lysate (TCL) was immunoblotted for checking equal use of proteins. The molecular weight markers are labeled in kilodaltons. b SW480 and RKO cells were treated with or without H2O2 (final conc. 100 μM) for 30 min. The immunoprecipitated TNKS was subjected to in vitro PARP assay. The molecular weight markers are labeled in kilodaltons. c CRC cells were transfected with control or PrxII-1 siRNA and then immunoblotted (IB) for indicated proteins. d Intracellular H2O2 level was measured in RKO cells that had been transfected with control or APC siRNA. The cells were incubated with 5,6-chloromethyl-2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate at 37 °C for 1 h and then the dichlorofluorescein (DCF) fluorescence was analyzed with a flow cytometry. A representative cell sorting datum of three experiments is shown. e RKO cells were transfected with either APC siRNA alone or APC plus PrxII-1 siRNAs and then immunoblotted for indicated proteins. f RKO cells were transfected with control or APC siRNA and then treated with increasing concentrations of H2O2 for 10 min. The immunoprecipitated TNKS was subjected to in vitro PARP assay. g HEK293 cells were transfected with plasmid vectors encoding TNKS1 WT and CS (Cys-to-Ser substitution) mutants and treated with or without 100 μM H2O2 for 10 min. The expressed Flag-TNKS1 enzymes were immunoprecipitated with anti-M2 (Flag) antibody and subjected to in vitro PARP assay. h Recombinant TNKS1-PARP proteins (aa 1023–1327) in E. coli extract were pooled down with glutathione-Sepharose 4B beads, incubated for 10 min in the presence or absence of 100 μM H2O2, and then subjected to in vitro PARP assay. The histone mixture (Coomassie blue staining) was used as substrate. i Purified recombinant TNKS1–PARP proteins were incubated with 500 μM H2O2 for zinc releasing assay as described in the Methods. Data in the graph are the average percent increases ± s.d. of free zinc ions vs. maximum zinc content in the purified GST–TNKS1–PARP protein used for the reaction (n = 3, *P < 0.001 with repeated measures ANOVA). Immunoblots (IB) or 32P-autoradiographs shown are a representative of three independent experiments. Total cell lysates (TCL) were immunoblotted as control for the amount of indicated proteins. Firefly luciferase-specific siRNA was used as control (C)
