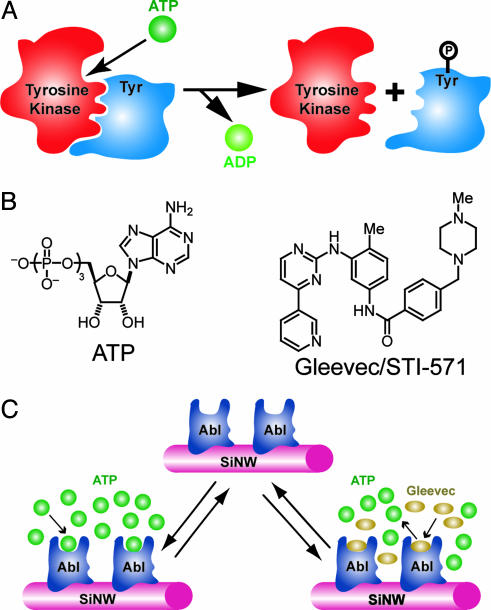
Fig. 1.
Detection of small-molecule–protein interactions for tyrosine kinases. (A) Scheme illustrating basic activity of a tyrosine kinase: ATP binds to the tyrosine kinase active site, and then the γ-phosphate group is transferred to the tyrosine (Tyr) residue of the substrate protein. (B) Structures of ATP and the small-molecule inhibitor of ATP binding to the Abl tyrosine kinase, Gleevec, or STI-571. (C) Detection of ATP binding and small-molecule inhibition of binding by using a SiNW sensor device. The tyrosine kinase Abl is covalently linked to the surface of a SiNW, and then the conductance of the nanowire device is monitored to detect ATP binding and the competitive inhibition of ATP binding by Gleevec.