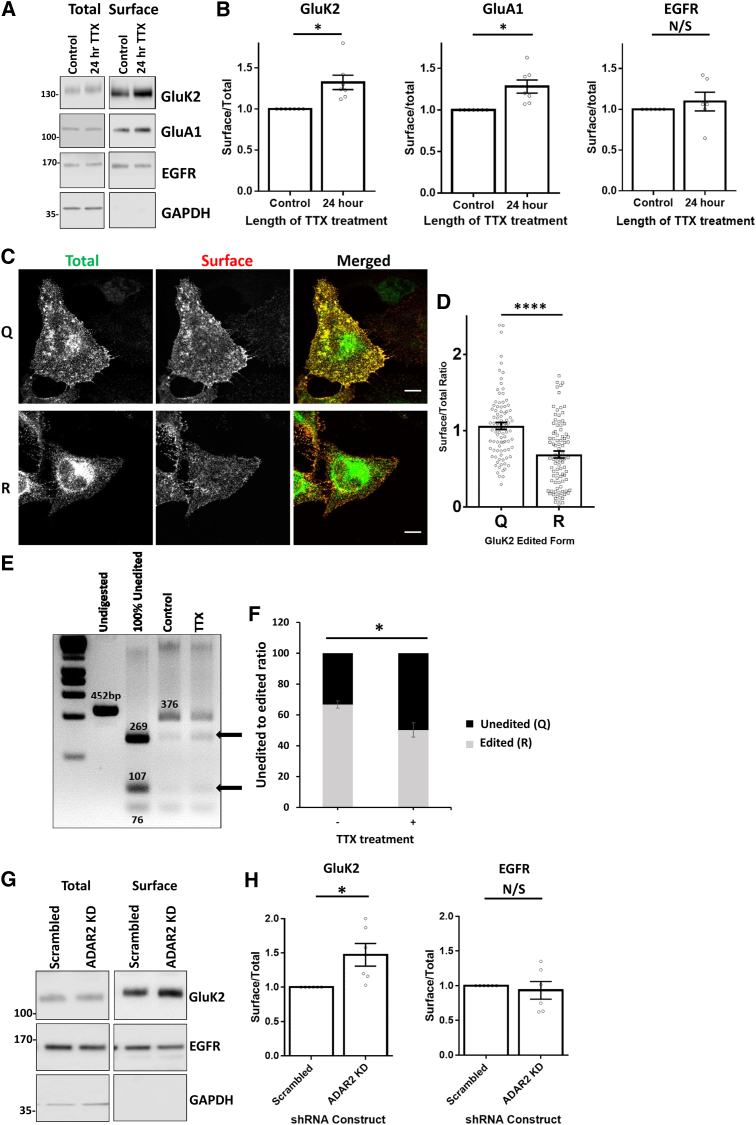
Figure 3.
KAR ER Exit Is Regulated by Activity-Dependent Changes in RNA Editing of GluK2
(A) Representative western blots of surface-biotinylated KAR and AMPAR subunits and EGFR in hippocampal neurons. The blots show surface and total levels of subunits with or without 24-hr treatment with 1 μM TTX to suppress synaptic activity.
(B) Quantification of immunoblots and comparison of surface-to-total ratios from six (GluA1 and EGFR) and seven (GluK2) independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05, Wilcoxon matched pairs signed-rank test.
(C) SBP-EGFP-GluK2 unedited (Q) or edited (R) RUSH constructs transfected into HeLa cells with addition of biotin at the time of transfection to allow basal expression. Surface RUSH KARs were labeled with anti-SBP for a duration of 5 min. See also Figure S3A.
(D) Quantification from (C), representative of three independent experiments (n = 90). ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, Welch’s t test.
(E) RT-PCR and digestion analysis of levels of unedited and edited GluK2 with or without TTX treatment. Black arrows indicate unedited forms of GluK2.
(F) Quantification of unedited and edited GluK2 with or without TTX treatment (n = 5). ∗p < 0.05, Welch’s t test.
(G) Representative western blots of surface-biotinylated GluK2 and EGFR after lentiviral infection of primary hippocampal neurons with either scrambled or ADAR2-targeting shRNA. The blots show both total and surface levels of GluK2 and EGFR after 5 days of knockdown. See also Figure S3B.
(H) Quantification of immunoblots and comparison of surface-to-total ratios from six independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05, Wilcoxon matched pairs signed-rank test.