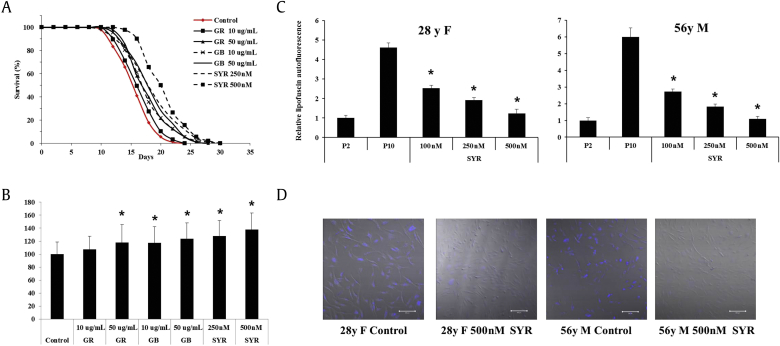
Fig. 5.
Ginseng components have potent antiaging activity. Ginseng root, ginseng berry, and syringaresinol induce a life span extension in the Caenorhabditis elegans wild type N2 strain. The survival curves (A) and the mean life span (B) are presented. The data were analyzed via a Kaplan–Meier survival analysis. The mean adult life span of each condition is (mean ± standard deviation) as follows: N2 control, 16.2 ± 3.0 d; GR 10 μg/mL, 17.4 ± 3.3 d; GR 50 μg/mL, 19.1 ± 4.5 d; GB 10 μg/ml, 19.0 ± 4.1 d; GB 50 μg/mL, 20.1 ± 4.0 d; SYR 250nM, 20.8 ± 3.9 d; and SYR 500nM, 22.4 ± 4.1 d. * p < 0.05 by Peto's log–rank test. The data represent one experiment with two additional repeats. (C, D) Ginseng components decrease lipofuscin accumulation in passaged human dermal fibroblasts. Dermal fibroblasts from a 28-yr-old female and a 56-yr-old male were treated with 100–500nM of syringaresinol for 10 passages, and the accumulated age-related lipofuscin was measured (C) and visualized (D). The accumulated lipofuscin levels were detected using a confocal laser scanning microscope (Ex: 350 nm; Em: 420 nm). The fluorescence intensities of the cells were calculated densitometrically by measuring the average pixel intensity in each cell. The data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. * p < 0.05 by two-tailed Student t test. Em, Emission; Ex, Excitation; GB, ginseng berry extract; GR, ginseng root extract; SYR, syringaresinol.