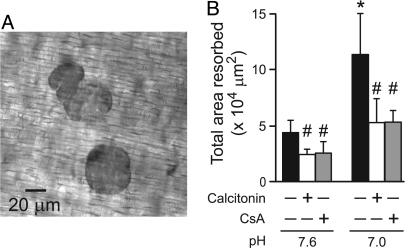
Fig. 6.
Role of NFAT in mediating the effects of acidosis on osteoclastic resorption. Rabbit osteoclasts were plated on dentin slices and treated with calcitonin (10 μM) or cyclosporin A (CsA, 1 μM) for 30 min at pH 7.6. In some samples, the pH was then altered to 7.0 by increasing the partial pressure of CO2 (respiratory acidosis). Experiments were stopped at 24 h, and the number of osteoclasts was assessed. The mean number of osteoclasts per slice was 170 ± 9, and no significant differences were observed among conditions. (A) Phase-contrast micrograph of resorption pits. (B) Quantification of the total area resorbed per slice. Data are means ± SEM, for three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. Differences were assessed by using Student's t test. *, Significant difference for the effect of acidosis; #, significant difference for the effects of calcitonin or CsA, compared with untreated samples at the same pH.