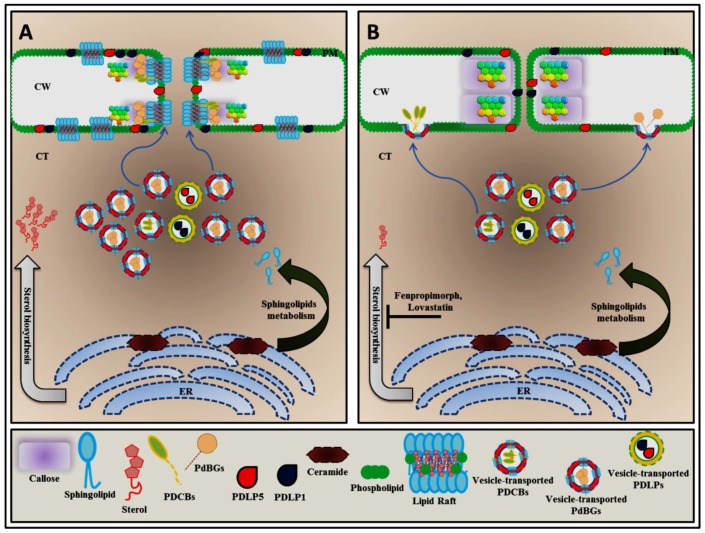
Figure 2.
Localization of GPI-anchored plasmodesmata (PD) proteins are controlled by lipid rafts. GPI-anchored PD proteins such as plasmodesmata callose binding (PDCB) proteins and plasmodesmal-localized β-1,3-glucanases (PDBGs) are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). These two proteins may require lipid raft–enriched vesicle-mediated exocytosis machinery to reach both the PD plasma membrane and the cellular plasma membrane as their target locations (A). An excessive sterol amount is able to induce the lipid raft–enriched vesicle-mediated exocytosis of PDCBs and PDBGs to regulate symplastic nanochannels by governing plasmodesmata callose (PDC) accumulation (A). The disruption of the sterol biosynthesis pathway with fenpropimorph or lovastatin affects the transport system of GPI-anchored PD proteins, preventing the proper localization of these two proteins (B).