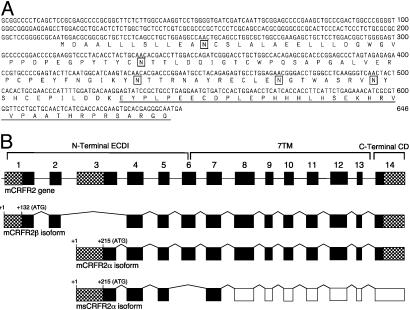
Fig. 1.
Sequence of sCRFR2α and genomic structure CRFR2. (A) Nucleotide and translated amino acid sequence of the sCRFR2α. Underlined amino acids indicate the unique C-terminal tail. Boxed residues indicate putative N-linked glycosylation sites. (B) Schematic representation of the structure of the mouse CRFR2 gene (first scheme), the two known functional transcripts in mouse, β and α (second and third schemes, respectively), and the sCRFR2α splice variant (fourth scheme). The locations of the translation start sites (ATG) are indicated. Exons coding for the N-terminal ECD (ECD1), the seven transmembrane domains (7TM), and the C-terminal cytoplasmic domain (CD) are indicated. 5′ and 3′ UTRs are indicated by hatched boxes. Black boxes represent coding regions, and white boxes represent exons downstream to the stop codon.