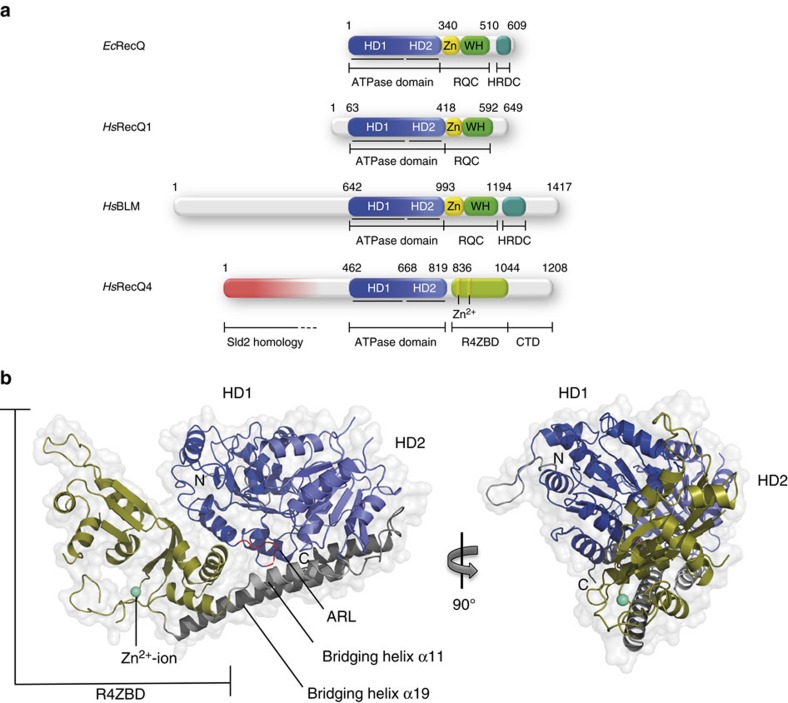
Figure 1. Overall structure of RecQ4.
(a) Comparison of the domain architecture of E. coli (Ec)RecQ and the Homo sapiens (Hs)RecQ helicases BLM, RecQ1 and RecQ4. The ATPase domain, comprising HD1 and HD2, is highly conserved among all RecQ proteins. Additional RecQ-conserved domains are the RQC domain (featuring the Zn2+-binding (Zn) and winged-helix (WH) subdomains) and the HRDC domain. In place of a RQC domain, RecQ4 features a structurally unique domain, termed RecQ4-Zn2+-binding domain (R4ZBD). Upstream of the helicase core, RecQ4 harbors the Sld2-homology domain at its N-terminus. Colour code: HD1—dark blue, HD2—light blue, Zn—yellow, WH—green, HRDC—turquoise, Sld2—red, R4ZBD—olive. (b) Structure of human RecQ4 (aa 449–1111) in cartoon representation. Colour code as in A. Two bridging helices, α11 and α19 connect the ATPase domain to the R4ZBD in a hinge-like fashion. The R4ZBD coordinates a Zn2+-ion (cyan sphere). The position of the ARL within HD1 is indicated and shown in red. N- and C-termini are indicated in both structures by the letters N and C, respectively. A complete annotation of secondary structure elements is provided in Supplementary Fig. 1. A stereo-view image of the R4ZBD including its electron density is shown in Supplementary Fig. 2.