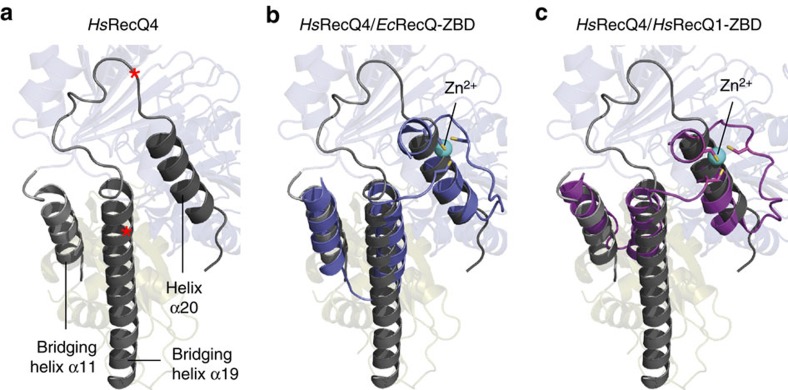
Figure 4. Three helices in RecQ4 mimic a RQC ZBD-like arrangement.
(a) The position of the two bridging helixes (α11 and α19) and helix α20 within the RecQ4 model are shown in dark grey. Red asterisks highlight the location of two early termination patient mutations (R1072X and Q1091X), which are associated with RAPADILINO syndrome (see Discussion). (b) Superposition of the three RecQ4 helices with the Zn-binding domain (ZBD) of EcRecQ (depicted in blue). (c) Superposition of the three RecQ4 helices with the Zn-binding domain (ZBD) of HsRecQ1 (depicted in magenta). (b,c) Bridging helix α11 and the downstream part of bridging helix α19 adopt the same position as the non-metal-coordinating helices, while helix α20 assumes the position of the in-line oriented Zn2+-coordinating helices of the respective ZBDs. Alignments where extracted from the structural alignment as shown in Fig. 3.