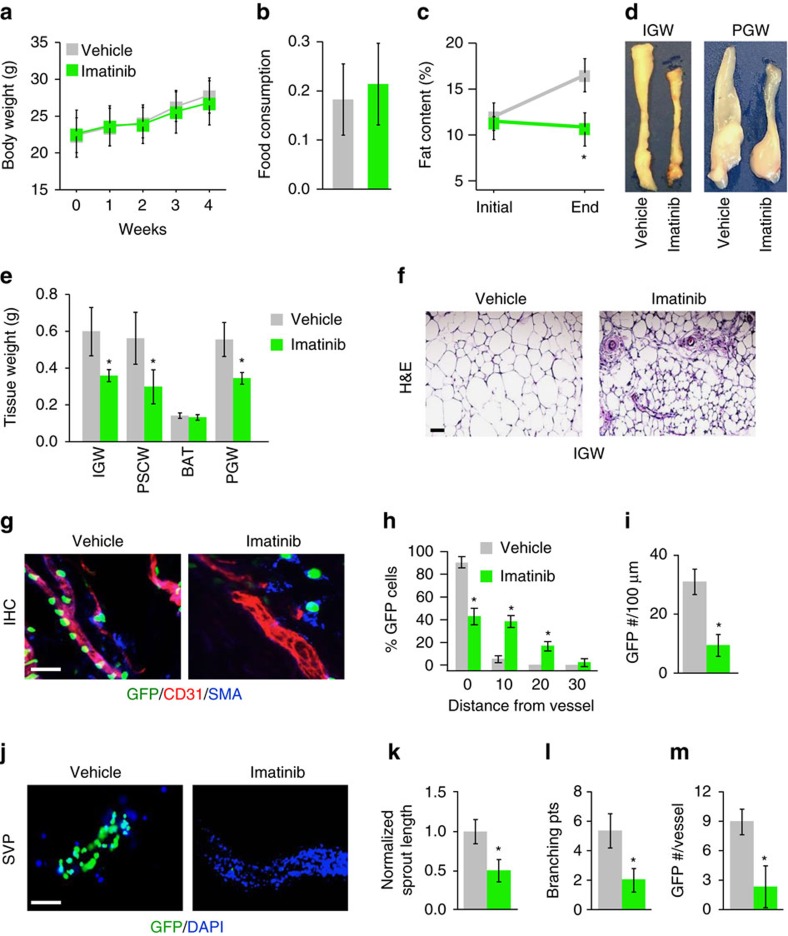
Figure 6. Pharmacologically blocking PDGFRβ disrupts APC niche interaction.
(a,b) One-month-old AT-GFP male mice were administered vehicle (5% dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO)) or imatinib (50 μg per mouse) by IP four times a week for 4 weeks. Experiments were performed three times on 8 mice per group. Body weight (a) and food intake (b) were measured. (c) Fat content of mice described in a before and end of treatment regime. (d,e) Representative adipose tissue images (d) and weights (e) from mice described in a. (f) Representative images of H&E staining from subcutaneous IGW depots from mice described in a. Scale bar 100 μm. (g) Sections from subcutaneous IGW depots from mice described in a were stained with CD31 and SMA and visualized for AT-GFP. Scale bar=100 μm. (h) Quantification of distance of AT-GFP+ cells away from CD31/SMA+ blood vessels from sections described in g. (i,j) SVPs were isolated from mice described in a and cultured. GFP locality was visualized 12 h later (j) and AT-GFP number was quantified (i). Scale bar=100 μm. (k–m) Subcutaneous IGW depots from mice described in a were excised and encased in Matrigel. Explants were continually treated with vehicle or imatinib ex vivo for 5 days. Vascular sprouts were then quantified for sprout length (k), branching (l) and progenitor occupancy (m). *P<0.01 Imatinib treated compared to vehicle (DMSO) treated. Data are expressed as means±s.e.m. Scale bars 100 μm.