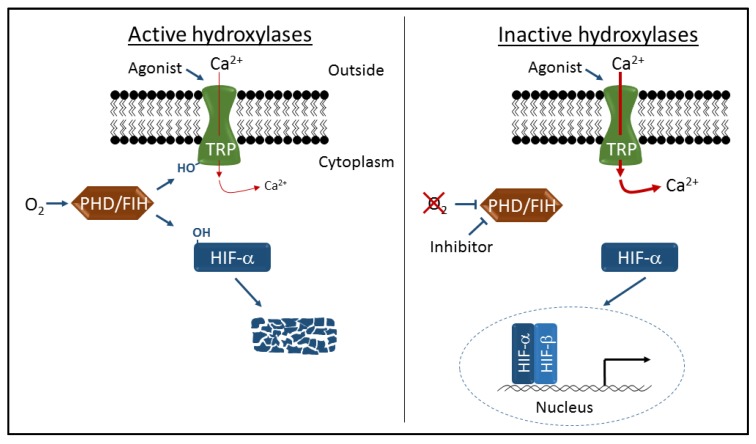
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of transient receptor potential (TRP) channel and hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) regulation by the prolyl hydroxylase containing enzymes (PHD) and asparaginyl hydroxylase factor inhibiting HIF (FIH) hydroxylases. Oxygen-dependent hydroxylation (-OH) of TRPA1 and TRPV3 channels inhibits cation entry through activated channels, and hydroxylation of HIFα proteins leads to proteolytic degradation and transcriptional repression. Inhibition of hydroxylase activity by hypoxia or specific inhibitors leads to increased cation entry and robust HIF-dependent gene activation.