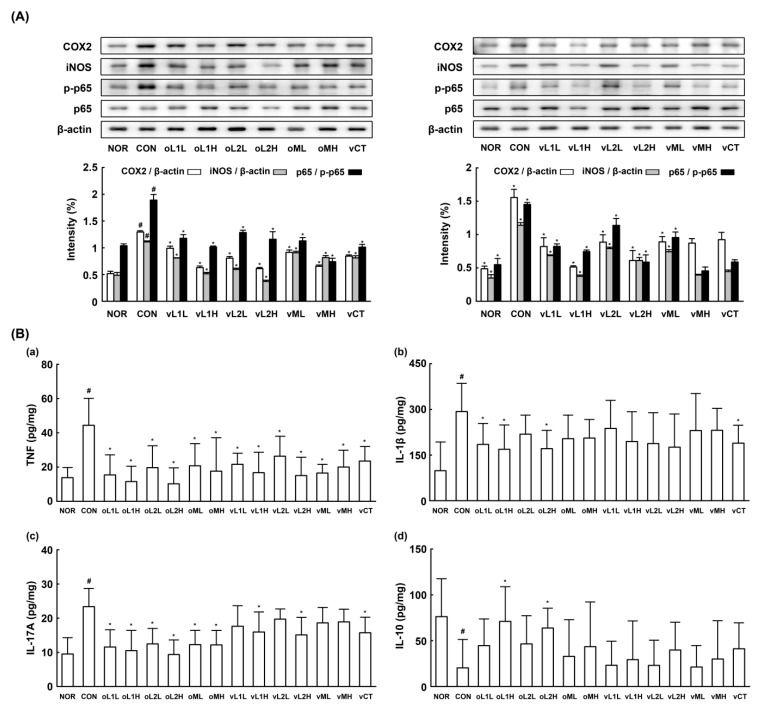
Figure 3.
Effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 (L1), Lactobacillus acidophilus La-14 (L2), and PM on the expressions of inflammatory cytokines, COX-2, and iNOS and the activation of NF-κB in the vaginas of G. vaginalis (GV)-infected mice. (A) Effect in COX-2 and iNOS expressions and NF-κB activation, analyzed by immunoblotting; (B) Effects in TNF-α (a), IL-1β (b), IL-17 (c), and IL-10 expressions, assayed by ELISA (d). Female mouse vaginas were infected with GV (1 × 108 CFU/mouse) except normal group (NOR, normal group treated with vehicle alone). Test agents (CON, vehicle alone; oL1L, orally administered L1; oL1H, orally administered 5 × 109 CFU/mouse of L1; oL2L, orally administered 5 × 108 CFU/mouse of L2; oLr2H, orally administered 5 × 109 CFU/mouse of L2; oML, orally administered 5 × 108 CFU of PM /mouse; oMH, orally administered 5 × 109 CFU of PM/mouse; vL1L, intravaginally administered 5 × 108 CFU/mouse of L1; vL1H, intravaginally administered 5 × 109 CFU/mouse of L1; vL2L, intravaginally administered 5 × 108 CFU/mouse of L2; vLr2H, intravaginally administered 5 × 109 CFU/mouse of L2; vML, intravaginally administered 5 × 108 CFU of PM/mouse; vMH, intravaginally administered 5 × 109 CFU of PM/mouse; and vCT, intravaginally administered 20 μL of 10% (v/v) clotrimazole) were administered once a day for 14 days. On day 15 post-infection, the mice were sacrificed. Inflammatory markers were assayed using ELISA and immunoblot analyses. All values were indicated as mean ± SD (n = 6). # Significantly different vs. normal group (p < 0.05). * Significantly different vs. control group (p < 0.05).