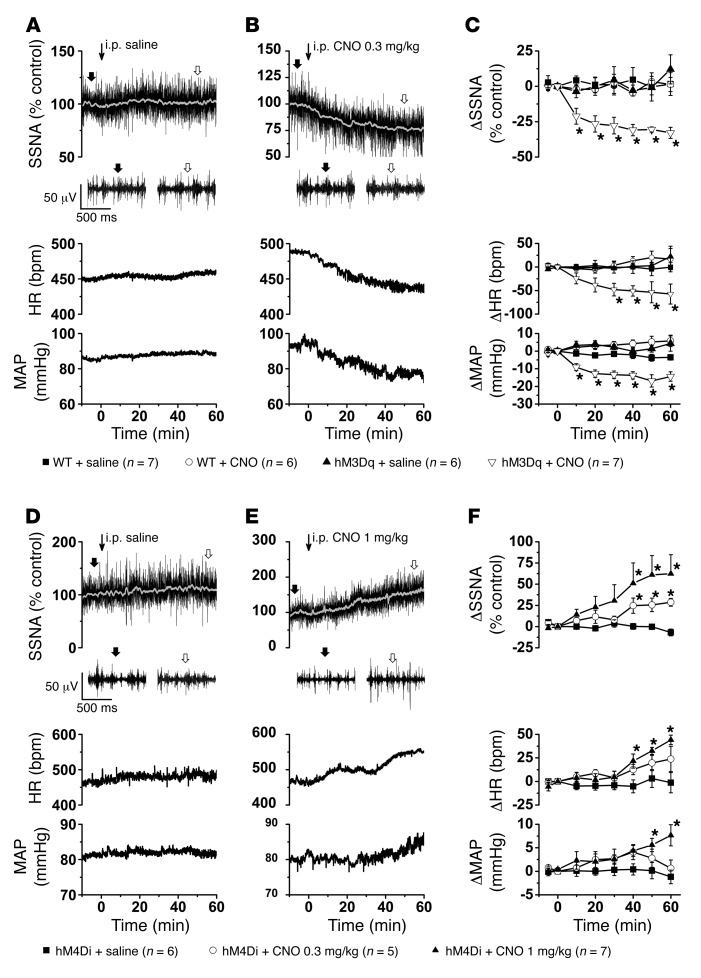
Figure 1. Selective activation and inhibition of ArcN NPY/AgRP neurons decreases and increases SNA, respectively.
(A) Representative experiment showing that i.p. injection of saline (at thin arrow) has no effect on raw SSNA, HR, and MAP in an ArcN hM3Dq mouse. Expanded raw nerve tracings, before and after injection, are indicated in this and all subsequent figures by filled and open arrows, respectively. (B) Representative experiment showing that i.p. injection of CNO (at thin arrow) in an ArcN hM3Dq mouse immediately decreases raw SSNA, HR, and MAP. (C) Grouped data showing that i.p. CNO, but not saline, decreases SSNA, HR, and MAP in ArcN hM3Dq mice. Neither saline nor CNO had effects in WT mice that received hM3Dq. Baseline values in WT mice (n = 13) were 88 ± 3 mmHg and 469 ± 13 bpm and in Agrp-IRES-Cre (n = 12) were 91 ± 3 mmHg and 460 ± 16 bpm. (D). Representative experiment showing that i.p. injection of saline (at thin arrow) has no effect on raw SSNA, HR, and MAP in an ArcN hM4Di mouse. (E) Representative experiment showing that i.p. injection of CNO (at thin arrow) in an ArcN hM4Di mouse increases raw SSNA, HR, and MAP. (F). Grouped data showing that i.p. CNO, but not saline, dose-dependently increases SSNA, HR, and MAP in ArcN hM4Di mice. Baseline values were 78 ± 3 mmHg and 466 ± 14 bpm (n = 11). *P < 0.05, compared with time 0.