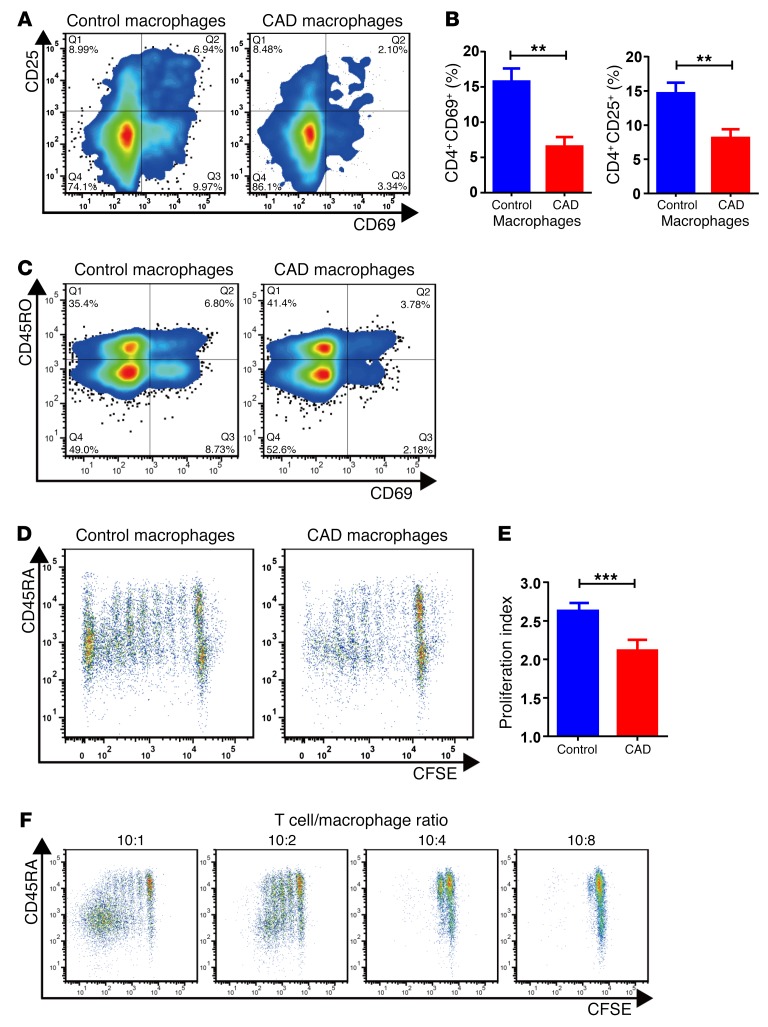
Figure 2. CAD macrophages fail to support activation and clonal expansion of CD4 T cells.
Macrophages were generated from monocytes from CAD patients and age-matched controls and cocultured with healthy purified CD4 T cells (macrophages: 10,000/well; T cells: 50,000/well). The stimulatory capacity of the macrophages was determined by the induction of CD69 and CD25 on T cells after 72 hours. T cell proliferation was quantified by CFSE dilution. (A) Representative flow cytometric data. (B) Frequencies of CD4+CD69+ and CD4+CD25+ T cells from 8 independent experiments. (C) Inhibitory effect of CAD macrophages on CD45RO– and CD45RO+CD4+ T cell populations. T cell activation was measured by the frequency of CD69+CD4+ T cells. Representative dot blots are shown. (D–F) T cell proliferation was quantified by CFSE dilution on day 6. (D) Representative dot blots. (E) Proliferation indices for 8 healthy controls and 13 patients with CAD. (F) The deficiency of T cell stimulation by CAD macrophages increased with increasing numbers of macrophages, suggestive of an active suppressive mechanism and not a reduced stimulatory capacity. Flow cytometric measurements of CFSE dilution in representative cocultures are shown. All data represent the mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001, by unpaired, 2-tailed Student’s t test.