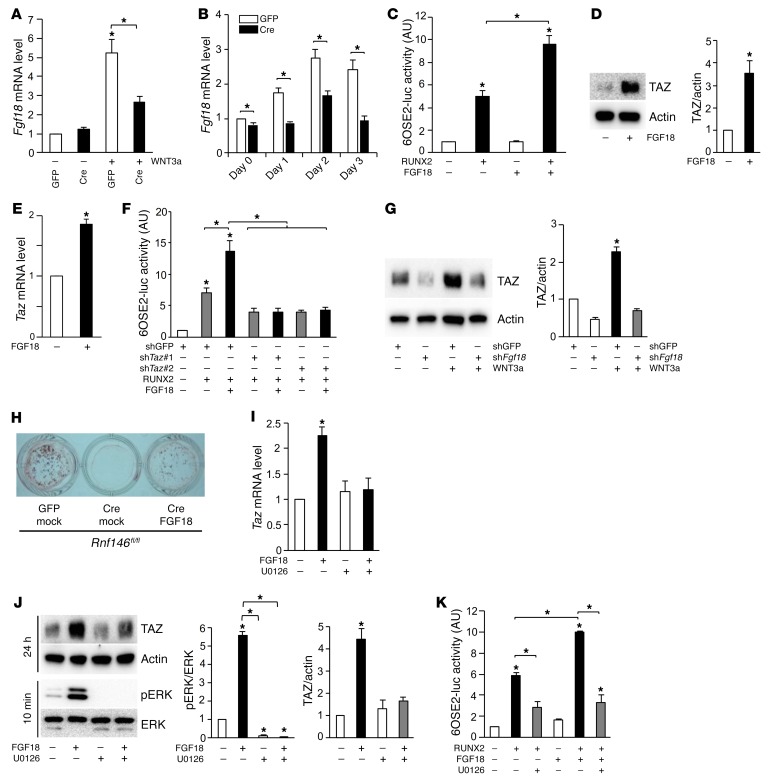
Figure 4. RNF146 regulates osteoblast differentiation through the FGF18-TAZ axis.
(A and B) qPCR analysis of Fgf18 mRNA expression in cells in Figure 3I (A) or C (B), cultured in osteogenic medium for 1–3 days. (C) Luciferase activity from an osteocalcin reporter assay in C2C12 cells transfected with or without RUNX2, and cultured in serum-free medium in the presence or absence of FGF18 (50 ng/ml). (D) Western blot analysis in primary murine osteoblasts cultured in serum-free medium in the presence or absence of FGF18 (50 ng/ml). (E) qPCR analysis of Taz mRNA expression in cells in D. (F) Luciferase activity from an osteocalcin reporter assay in C2C12 cells infected with shGFP or shTaz, transfected with or without RUNX2 and cultured in serum-free medium in the presence or absence of FGF18 (50 ng/ml). (G) Western blot analysis in primary murine osteoblasts infected with shGFP or shFgf18 and cultured in serum-free medium in the presence or absence of WNT3a (40 ng/ml). (H) Cells in Figure 3C, infected with an empty vector control (mock) or an FGF18-expressing retroviral vector were cultured in osteogenic medium and stained with alizarin red S solution. (I) qPCR analysis of Taz mRNA expression in primary murine osteoblasts cultured in serum-free medium in the presence or absence of FGF18 (50 ng/ml) and U0126 (10 μM). (J) Western blot analysis in cells in I cultured for 10 minutes or 24 hours. (K) Luciferase activity from an osteocalcin reporter assay in C2C12 cells transfected with or without RUNX2 and cultured in serum-free medium in the presence or absence of FGF18 (50 ng/ml) and U0126 (10 μM). n = 3. P values were determined by ANOVA with Tukey–Kramer’s post-hoc test (A, C, F, G, and I–K) or unpaired t test (B, D, and E). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05.