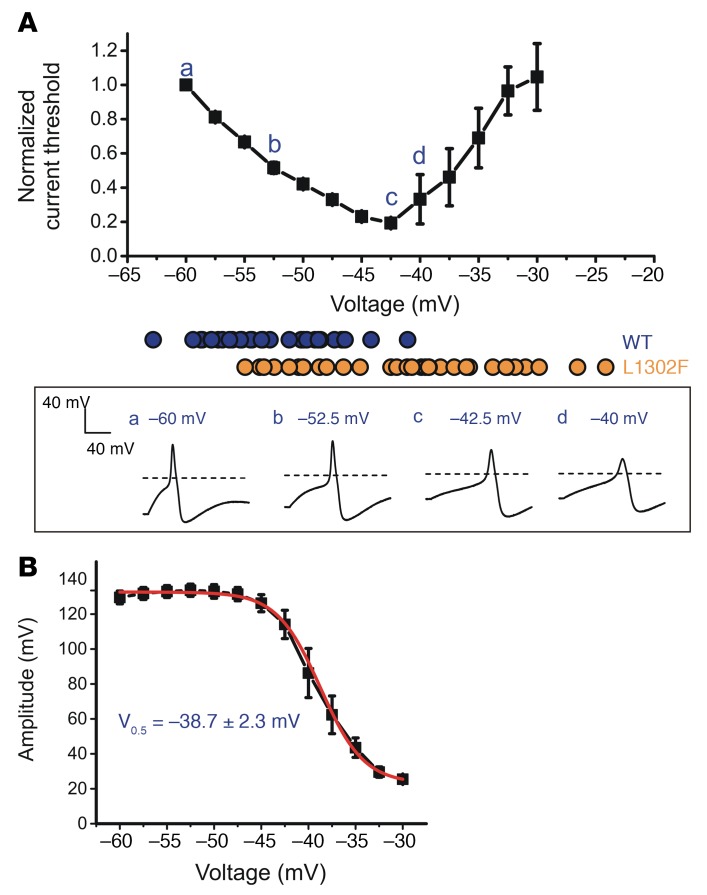
Figure 6. Depolarization of RMP causes biphasic changes in the current threshold and attenuates the action potential amplitude.
Small adult DRG neurons were held at membrane potentials ranging from –60 mV to –30 mV in 2.5-mV increments. The RMP distribution in WT- and L1302F-expressing neurons is illustrated by blue (WT) and orange (L1302F) solid circles. Action potential waveforms recorded at various voltages from representative cells are illustrated in the boxed panel below. (B) Action potential amplitude and resting membrane potential data were best fit by a single Boltzmann function with a midpoint voltage of –38.7 ± 2.3 mV. Data points in A and B represent mean values (n = 5), and error bars indicate the SEM.