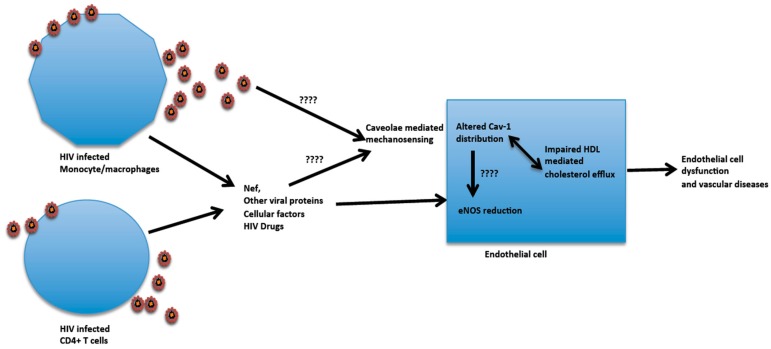
Figure 2.
HIV influence on aortic endothelial cell Cav-1 functions and potential link to pathogenesis. Viral proteins released from infected cells in combination with the induction of cellular factors such as cytokines and chemokines in the microenvironment can promote changes in Cav-1 cell distribution that impairs high-density lipoprotein (HDL) mediated cholesterol efflux and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) regulation. There is also a reduction in eNOS, which could be related to Cav-1 redistribution. The mechanosensing function of Cav-1 may be an alternative or additional mechanism that leads to Cav-1 redistribution. These HIV induced endothelial cell dysfunctions through Cav-1 can be contributing factors to vascular diseases in HIV infected individuals.