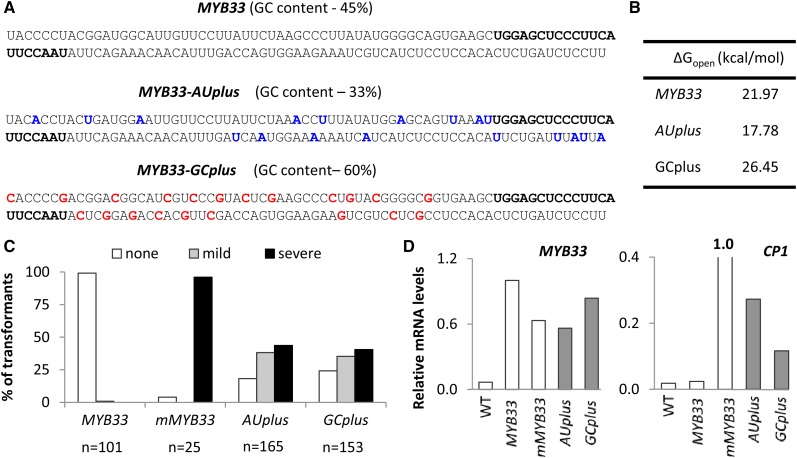
Figure 3.
Changes to AU content perturb miR159 silencing of MYB33. A, MYB33 transgenes with elevated AU content (MYB33-AUplus) and elevated GC content (MYB33-GCplus) in the vicinity of the miR159 target site (bold) were generated, changing only nucleotides occupying wobble positions. B, As a measure of their accessibility, ∆Gopen values were calculated for the miR159 target site in each construct using the Vienna RNAup web server. These values are a prediction of the energy required to unpair all nucleotides in a 51-nucleotide window comprising the miR159 binding site plus 17 nts 5′ and 13 nts 3′. C, The number of 24-d-old primary transformants of AUplus and GCplus falling into each phenotypic category (none, mild, or severe), as a percentage of the total number of transformants generated for each construct (n). Primary transformants of an endogenous MYB33 transgene (MYB33) or a miR159-resitant MYB33 transgene (mMYB33) were grown in parallel as controls. D, MYB33 and CP1 transcript levels, normalized to CYCLOPHILIN mRNA abundance, were measured in total RNA samples derived from 30 to 50 randomly selected 8-d-old transformants for each construct. Data are the averaged of three technical replicates.