FIGURE 2:
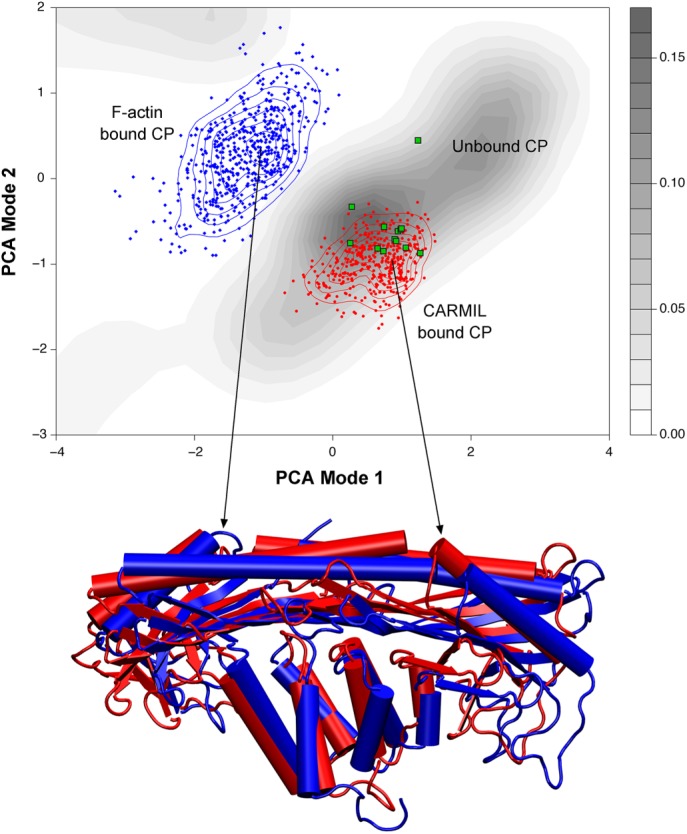
Principal component analysis (PCA) of CP. Top, PCA of molecular dynamics simulations of the structural conformations of CP. The simulations were begun with CP that was either free (gray contour shading), bound to F-actin (blue dots and contour lines), or bound to CARMIL (red dots and contour lines). The results were projected onto the same conformational space; existing CP structures were overlaid as green dots. Based on this analysis, CARMIL-bound CP exists in a conformational space more like that of unbound CP (gray) than to that of F-actin–bound CP. Bottom, overlay of protein structures, depicting the conformations that correspond to the peaks of CARMIL-bound and F-actin bound CP. This analysis supports the findings that CARMIL allosterically inhibits CP by eliciting changes to the actin-binding surface, holding CP in a conformation similar to the free state. Used with permission from Kim et al. (2012).
