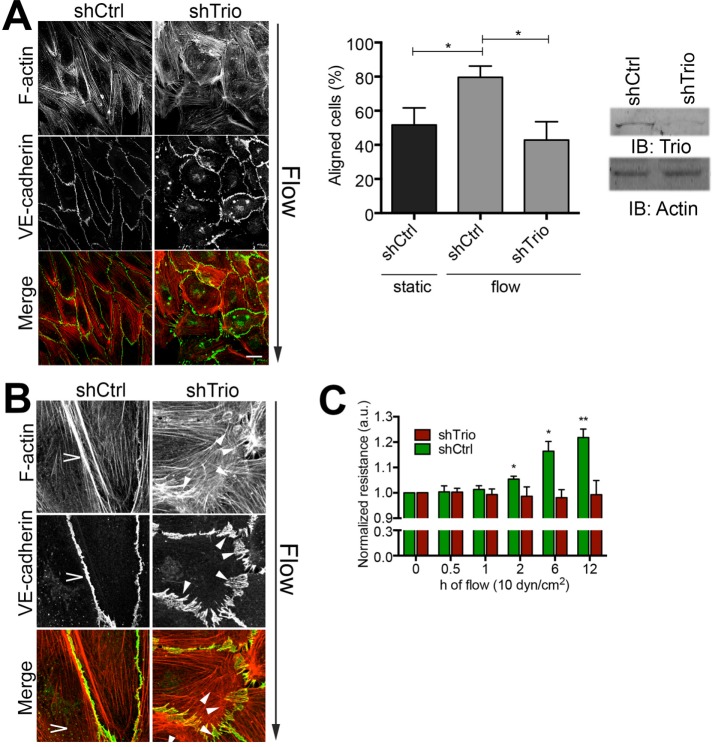
FIGURE 2:
Trio silencing inhibits flow-induced EC alignment. (A) Left, HUVECs treated with Ctrl and Trio shRNA (shCtrl and shTrio) were applied to flow for 12 h. Direction of flow is from top to bottom. Trio-deficient ECs failed to align. Bar, 25 μm. Middle, quantification of EC alignment upon flow vs. static conditions. Cells orientated between 0 and 45° are quantified as aligned. Data are mean of three independent experiments ± SEM. *p < 0.05. Right, Trio depletion with shRNA analyzed by Western blotting; actin is used as loading control. (B) Magnification of EC–cell junctions. Flow induces linear junction (open arrowhead), marked by VE-cadherin in green and F-actin in red. Depletion of Trio (shTrio) results in unstable, zipper-like junctions (closed arrowheads). Bar, 25 μm. (C) Resistance measurements using ECIS under flow conditions as indicated show that flow promotes EC resistance in time (green), whereas ECs depleted for Trio failed to increase flow-induced barrier resistance in time. Data are mean of three independent experiments ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.