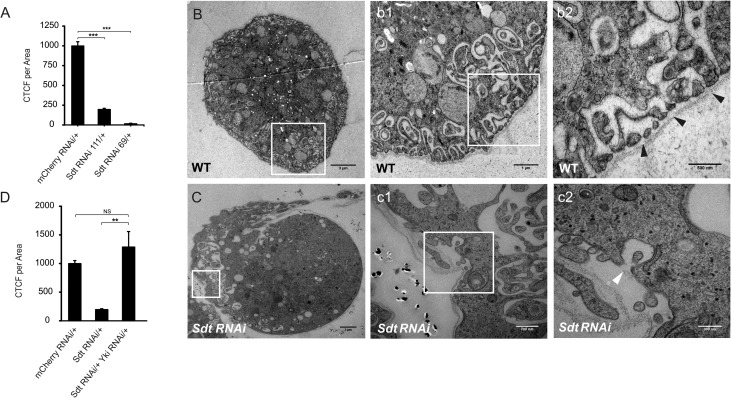
Figure 5.
Stardust (Sdt) knockdown in Drosophila results in dysfunctional nephrocytes. (A) In comparison to the control strain (mCherry RNAi/+), depletion of Stardust (Sdt RNAi 111/+ and Sdt RNAi 69/+) led to strongly reduced filtration rates in RFP accumulation assays. CTCF, corrected total cell fluorescence. (B–C) Transmission electron microscopy analysis of wildtype (B) and Sdt-depleted nephrocytes (C) demonstrated that the defects in RFP endocytosis are accompanied by malformation of slit-diaphragm–like structures in Sdt RNAi nephrocytes ([C] and details in c1–c2; scale bars, 3 µm, 700 nm, and 300 nm, respectively) compared with the wildtype control ([B], details in b1–2; scale bars, 3 µm, 1 µm, and 500 nm, respectively). (D) Parallel downregulation of Yki in Sdt RNAi nephrocytes (Std RNAi/+ Yki RNAi/+) completely rescued the defect in RFP filtration shown in (A). For each genotype, >50 nephrocytes from at least six individuals were scored.