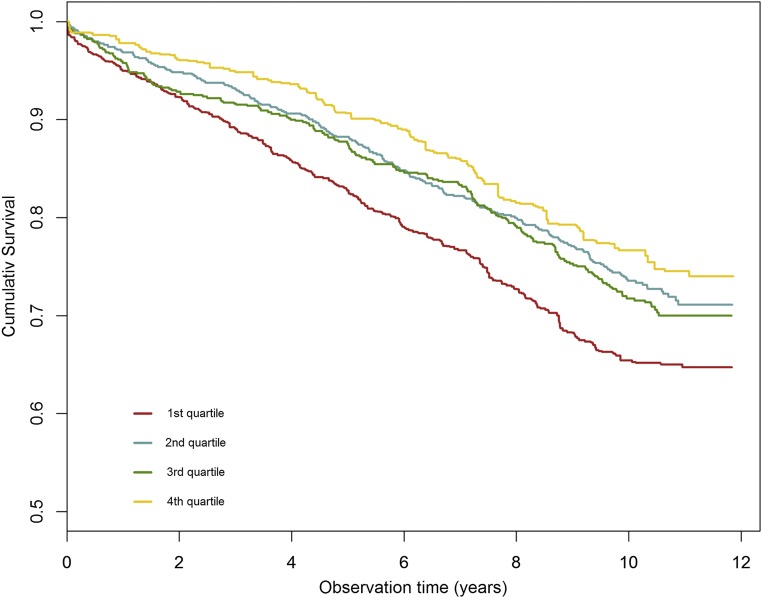
Figure 3.
Lower serum uromodulin is associated with higher mortality. Adjusted survival curves for all-cause mortality. Quartiles of serum uromodulin were balanced for age, sex, BMI, diabetes mellitus, smoking, eGFR, hypertension, and medication by inverse variance weighting. HRs for the second, third, and fourth quartiles compared with the first quartile were 0.74 (95% CI, 0.67 to 0.81), 0.79 (95% CI, 0.72 to 0.86), and 0.64 (95% CI, 0.58 to 0.70), respectively. The P value of the robust score test was <0.001.