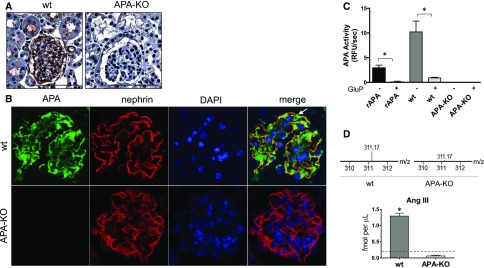
Figure 3.
Lack of expression and activity of APA were verified in APA-KO mice. Examination of APA expression by (A) immunohistochemistry in kidney sections of wild-type (wt) and APA-KO mice showed glomerular and apical tubular distribution of APA in wt mice and negative staining in APA-KO mice. Scale bars, 200 µm. Examination by (B) immunofluorescence revealed colocalization of APA with nephrin, a podocyte marker, in wt mice and lack of glomerular APA expression in APA-KO mice. The white arrow indicates the body of the podocyte only showing APA staining (green), whereas colocalization of APA and nephrin corresponds to the podocyte slit diaphragms (yellow). DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. Fluorometry-based APA enzymatic activity (C) was measured in whole-kidney homogenates harvested from wt or APA-KO mice. Bars represent mean values, and error bars show SEMs. APA activity was measured with or without the presence of the APA inhibitor glutamate phosphonate (GluP; 10 μm). Recombinant aminopeptidase A (rAPA) was used as a positive control. (D) Conversion of AngII into AngIII was verified by LC-MS/MS, showing detection of AngIII (represented by the +3 parent ion 311.17 m/z) in glomerular suspensions of wt mice and almost complete absence of AngIII in those of APA-KO mice. The horizontal dashed line in the bar graph denotes the lower limit of detection. *P<0.001.