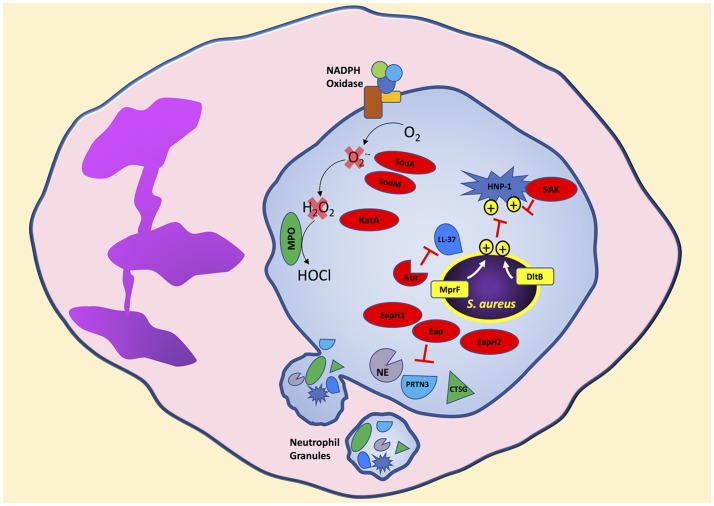
Figure 2.
S. aureus produces virulence factors that target different neutrophil bactericidal mechanisms following phagocytosis. Cationic antimicrobial peptides are ineffective toward S. aureus due to the presence of positive charges on the bacterial surface transferred by MprF and DltB. S. aureus secretes virulence factors that degrade antimicrobial proteins and enzymes released into the neutrophil phagosome. In addition, neutrophil reactive oxygen species production is decreased by S. aureus virulence factors that degrade intermediate reactive oxygen species like superoxide and hydrogen peroxide to reduce the formation of the highly bactericidal chemical agent hypochlorous acid. Bacterial components indicated in red. Aur, aureolysin; PRTN3, proteinase 3; CTSG, cathepsin G; SAK, staphylokinase.