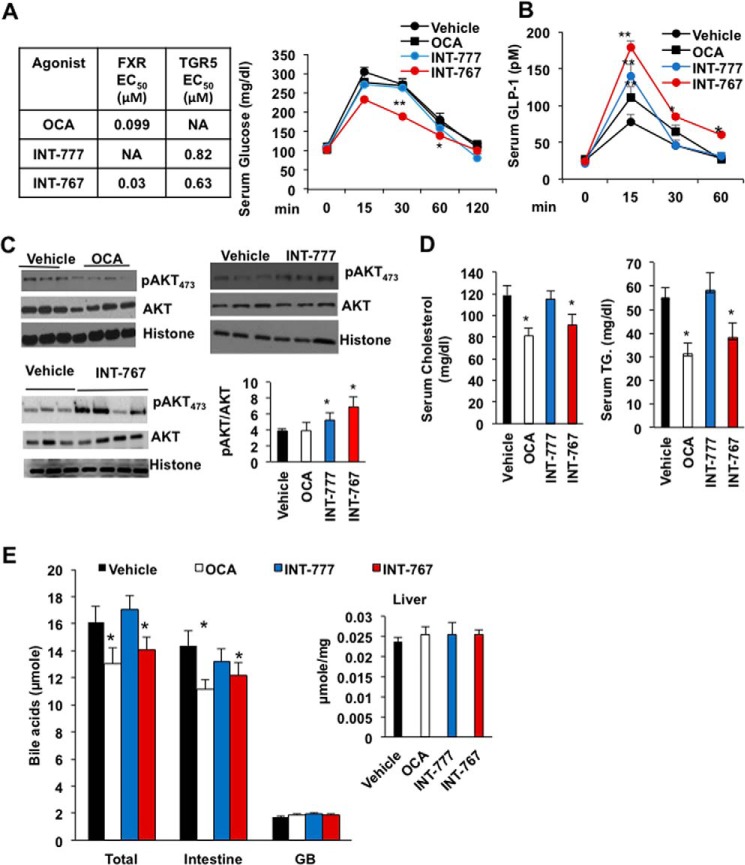
Figure 1.
INT-767 stimulates glucose and hepatic insulin signaling in mice. Wild-type C57BL/6J mice were orally gavaged with the dual FXR and TGR5 agonist INT-767 (30 mg/kg, n = 10), FXR agonist OCA (30 mg/kg, n = 10), TGR5 agonist INT-777 (30 mg/kg, n = 8), or vehicle (5% CMC in water or 0.2% DMSO, n = 15) as described under “Experimental procedures.” A, efficacy of FXR-selective agonist OCA, TGR5-selective agonist INT-777, and dual FXR and TGR5 agonist INT-767, and effects of these agonists on oral glucose tolerance test in wild-type mice. B, serum GLP-1 assay of wild-type mice. C, AKT phosphorylation assay of liver lysates from ligand-treated wild-type mice. Each lane represents lysates from single mouse liver. D, OCA and INT-767 reduced serum cholesterol and triglyceride level. E, OCA and INT-767 reduced bile acid pool size. Intestine, liver, and gallbladder were isolated from mice (n = 8) treated with FXR agonists (30 mg/kg), and bile acid contents were assayed. The total bile acid pool includes bile acids in the intestine, liver, and gallbladder. Results were expressed as means ± S.E. * indicates statistically significant difference of treated versus vehicle control, p ≤ 0.05, and ** indicates p ≤ 0.01. Student's t test was used for statistical analysis.