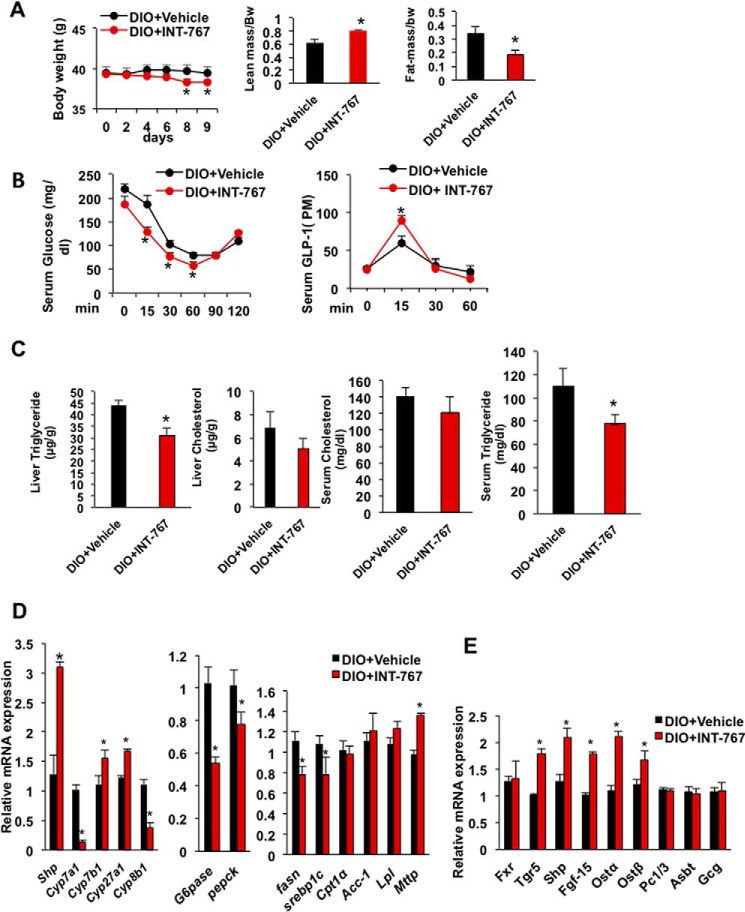
Figure 8.
INT-767 improved obesity, insulin sensitivity, and hepatic metabolism in diet-induced obese mice. C57BL/6J mice were fed a high fat diet for 5 months (DIO). A group of mice were gavaged with 30 mg/kg INT-767 (n = 9) or vehicle (n = 9) for 9 days, and mice were killed after 6 h of fasting. A, INT-767 reduced body weight and increased lean mass and reduced fat mass in DIO mice as measured by EchoMRI. B, INT-767 improved insulin tolerance and GLP-1 secretion in DIO mice. C, INT-767 significantly reduced triglyceride and tends to reduce liver cholesterol and serum triglyceride and cholesterol levels. D, INT-767 altered liver bile acid synthesis and fatty synthesis and mRNA expression. E, INT-767-induced FXR target gene mRNA expression in mouse intestine. Real-time PCR analysis of liver and intestine mRNA is relative to vehicle control as 1. All results were expressed as means ± S.E. Statistical significance was calculated using Student's t test. * indicates significant difference INT-767-treated versus vehicle control, p ≤ 0.05.