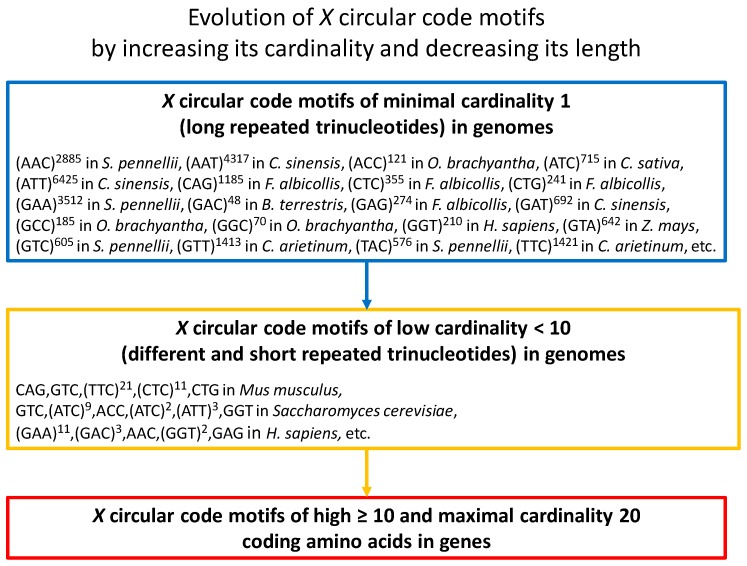
Figure 1.
Model of evolution of the circular code motifs (Equation (1)) by increasing its cardinality (composition) and decreasing its length. Evolution begins with motifs of minimal cardinality 1 (long repeated trinucleotides) in genomes (the examples given are extracted from Table 2 in [8]). Then, the mutations in repeated trinucleotides lead to motifs of low cardinality (different and short repeated trinucleotides) in genomes (the examples given are extracted from Table 4 in [8]) up to motifs of high and maximal cardinality 20 coding the 12 amino acids (Equation (2)).