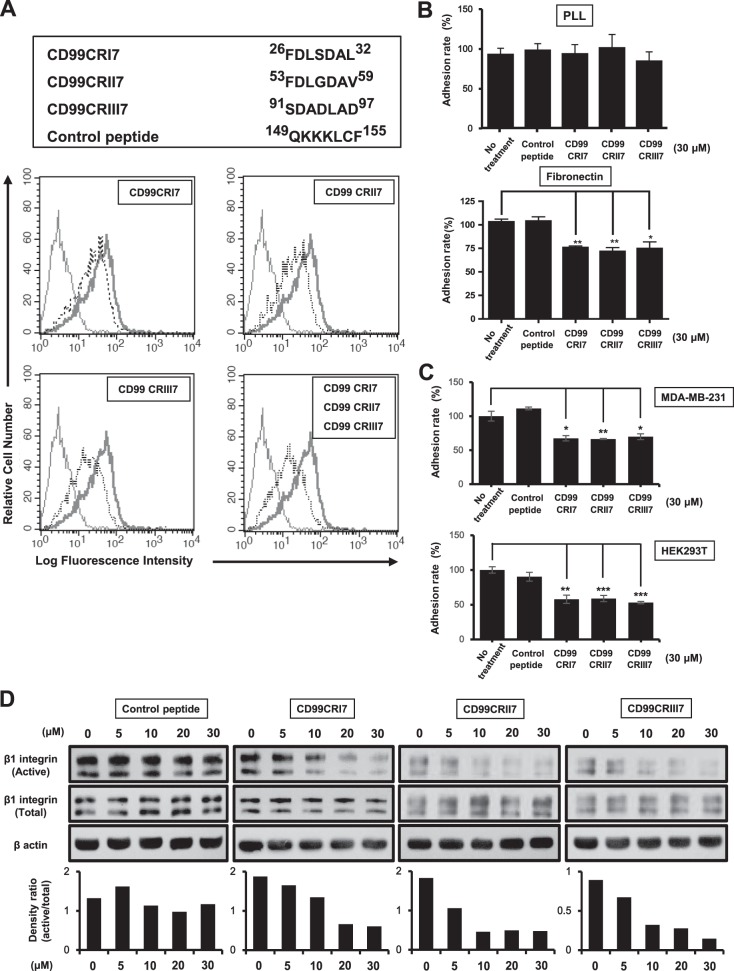
FIG 2.
The ability of CD99 agonistic peptides to suppress β1 integrin activity is comparable to that of CD99-Fc proteins. (A) The sequences of 7-mer synthetic peptides are shown at the top. To assess the binding of CD99-derived peptides CD99CRI7, -II7, and -III7 to CD99 expressed on MCF-7 cells, a competition assay with a purified recombinant CD99-Fc I fusion protein was performed. The ability of CD99-Fc fusion proteins to bind to cell surface CD99 was measured by flow cytometry to evaluate the occupation of CD99 by CD99-derived peptides. Light solid line, negative control; heavy solid line, control peptide; dotted line, competition with peptide. (B, C) Cell attachment to the ECM was analyzed by adhesion assay on fibronectin as described above. Results were replicated in three independent experiments. Asterisks represent statistically significant differences from untreated cells as follows: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. (D) MCF-7 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of peptides (0 to 30 μM) for 1 h. Cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting with the antibodies indicated. The graphs show the active β1 integrin intensities of bands normalized against that of the total form. β-Actin was used as a loading control.