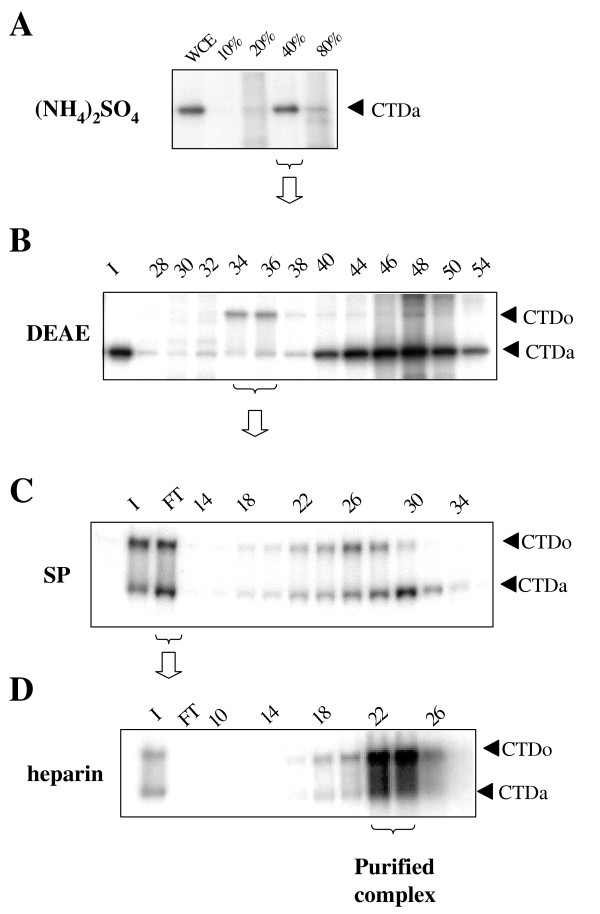
Figure 1.
Purification of Tat Associated CTD Kinase. A, Ammonium sulfate fraction of T-cell extract. Whole cell extract of Jurkat T cells was fractionated by ammonium sulfate added sequentially to 10%, 20%, 40% and 80% saturation as described in Experimental procedures. Fractions were analyzed for Tat-associated CTD kinase activity as described in the Experimental procedures section. A portion of each fraction was bound to GST-Tat 72 immobilized on glutathione-agarose beads and then incubated with [γ-32P] ATP and recombinant GST-CTD. Phosphorylated GST-CTD was resolved on SDS/10%-(w/v)-PAGE. B, DEAE-Sepharose column-chromatographic elution profile. Jurkat T-cell extract 40%-(NH4)2SO4 cut was applied to a DEAE-Sepharose column. Fractions were analyzed for Tat-associated CTD kinase activity as described above. C, SP-Sepharose column-chromatographic elution profile. DEAE-fractions 32 to 36 containing hyperphosphorylating CTD kinase activity were combined and applied to SP-Sepharose column. D, heparin-agarose column-chromatographic elution profile. SP-Sepharose flow-through fraction was collected and further fractionated on Hi Trap heparin column. Fractions 22 to 24 (labelled as purified complex) contained Tat-associated CTD hyperphosphorylating activity. Positions of CTDa and CTDo are shown. The figure is an autoradiogram.