Figure 1.
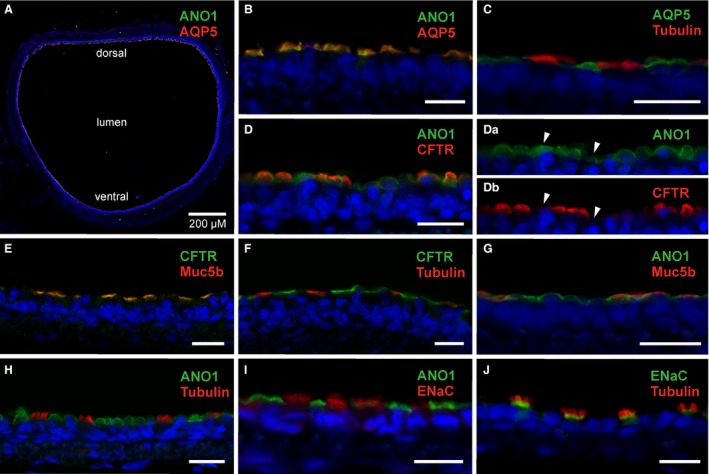
Cellular localization of secretory proteins in rat tracheal epithelium. (A) A cross‐section of the medial part of the rat trachea with immunosignals for ANO1 and AQP5 at the apical surface of the tracheal epithelium. (B) Immunosignals of ANO1 and AQP5 merge in cells stained in the surface epithelium. (C) AQP5 is not expressed in α‐tubulin‐positive ciliated cells. (D) ANO1‐ and CFTR‐immunosignals merge in most cells, but some show only ANO1 signals. (Da), (Db) Separate display of ANO1‐ and CFTR‐ immunofluorescence channels illustrates that some ANO1‐positive cells are CFTR‐negative (arrowheads). (E) CFTR‐ and Muc5b‐ immunosignals merge to produce a yellow signal in all stained cells. (F) CFTR‐ and α‐tubulin‐immunostainings label different cells, no merged signals are discernible. (G) ANO1 and Muc5b immunosignals appear colocalized in some cells, but other ANO1‐positive cells are Muc5b‐negative. (H) ANO1 is absent from α‐tubulin‐positive ciliated cells. (I) ANO1‐ and ENaC‐ immunosignals are localized in different cell types. No merged signal is discernible. (J) The ENaC‐specific immunosignal emanates from a distinct layer at the basal region of α‐tubulin‐expressing cilia. Blue signals show DAPI nuclear stain. Scale bars for B–J indicate 10 μm.
