FIGURE 10.
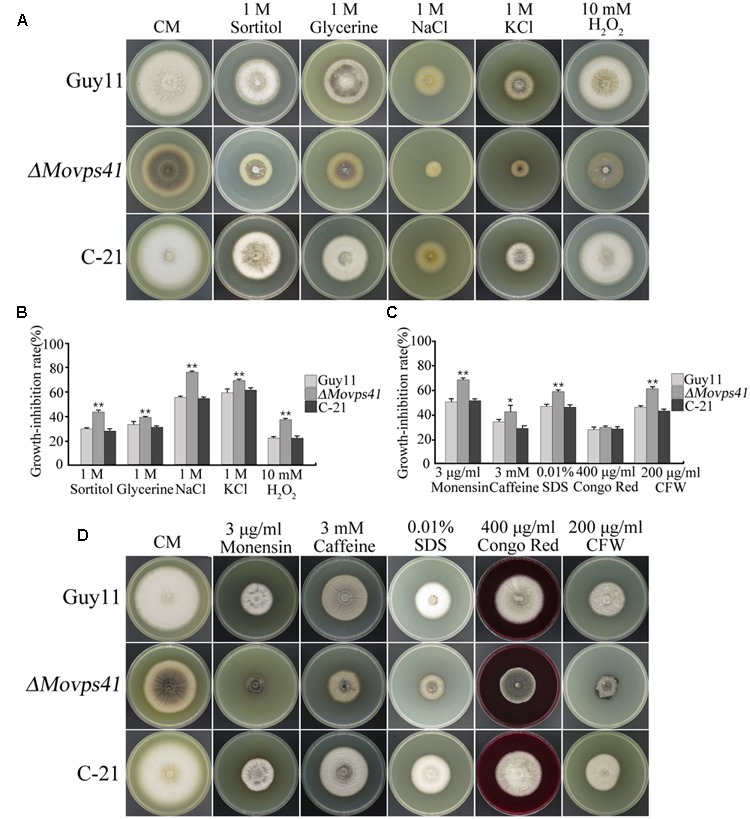
ΔMovps41 mutant displayed high sensitivity toward osmotic and oxidative stress inducing osmolytes. (A) Portrays vegetative growth attributes of ΔMovps41 mutant, wild-type and C-21 complementation strain on CM plates supplemented with (1 M sorbitol, 1 M glycerine, 1 M NaCl, and 1 M KCl), (B) Shows the statistical analysis of ΔMovps41 mutant, wild-type and C-21 complementation strain growing on CM plates supplemented with (1 M sorbitol, 1 M glycerine, 1 M NaCl, and 1 M KCl), The experiment was performed at least three biological repeats. Error bar represent the standard deviation between the ΔMovps41 mutant, wild-type and C-21 complementation strain and double asterisks represent P < 0.01. (C) Statistical computation of growth response of 1Movps41 mutant, wild-type and C-21 complementation strain on CM plates supplemented with osmolytes (0.01% SDS, 400 μg/mL Congo red, and 200 μg/mL Calcofluor white (CFW). The experiment was performed at least three biological repeats. Single asterisks represent P < 0.05, whilst double asterisks represent (P < 0.01). (D) Displays the growth performance of ΔMovps41 mutant, wild-type and C-21 complementation strain on CM plates supplemented with cell wall stress inducing osmolytes (0.01% SDS, 400 μg/mL Congo red, and 200 μg/mL Calcofluor white (CFW).
