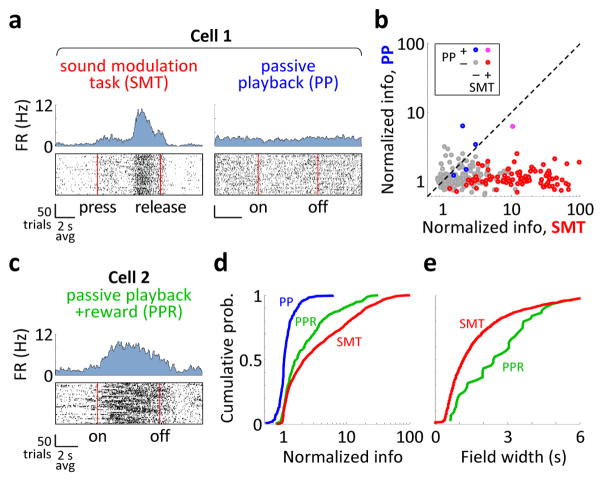
Figure 3. Activity depends on the behavioral context.
a) Activity of the same CA1 neuron in the SMT and during passive playback (PP) of acoustic stimuli that matched those in the SMT. Top: PSTHs. Bottom: Raster plots, with time linearly warped between the press and the release of the joystick. FR: firing rate; on: sound onset; off: sound offset. b) Firing rate modulations of all 295 CA1 neurons recorded in the SMT and PP. ‘Normalized information’ is the mutual information between spikes and the phase of the task, divided by the average value from samples with shuffled spike timing. Points are colored according to whether the cell’ was SMT-modulated and whether it was modulated by PP. c) Activity of a neuron during passive playback of acoustic stimuli that were followed by rewards (PPR). d) Cumulative histograms of the normalized information in the three tasks (295 cells for SMT and PP and 248 cells for PPR). e) Cumulative histograms of the field durations in the SMT and the PPR. Activity shows progressively stronger and temporally precise task modulation in the PP, PPR, and SMT tasks.