Figure 5.
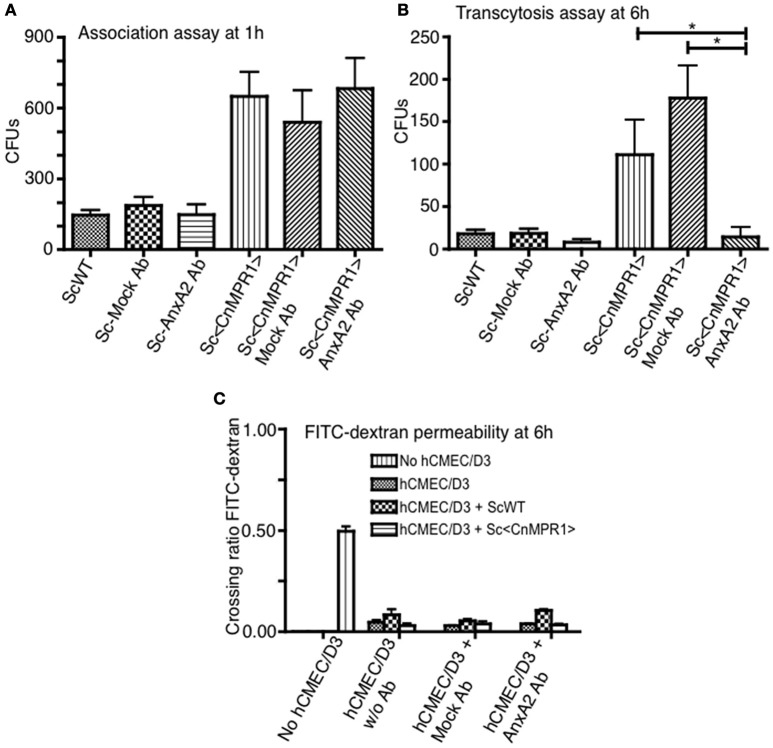
Inhibition of Annexin A2 (AnxA2) does not prevent the association of Sc<CnMPR1> with hBMECs but reduces the transcytosis of Sc<CnMPR1>. The in vitro models of BBB were used to investigate the association (A) and the transmigration of Sc<CnMPR1> across the BBB (B). The hBMECs were pretreated with the anti-AnxA2 or the IgG control antibody (mock treatment) for 40 min and subsequently incubated with ScWT or Sc<CnMPR1> at 37°C with 5% CO2. Non-pretreated hBMECs were used as a control for both assays. (A) At 1 h post-co-incubation, hBMECs were extensively washed to remove unattached Sc, lysed, and plated on YPD agar for CFU counting; CFUs corresponded to the number of Sc associated with hBMECs. Blocking AnxA2 activity with an anti-AnxA2 antibody did not affect the association of Sc<CnMPR1> with hBMECs (P > 0.05, n = 8). (B) At 6 h post-co-incubation transcytosis assays were performed where the cell culture media in the abluminal chambers of the in vitro BBB model was collected and plated on YPD agar. The CFU count showed a significant reduction of Sc<CnMPR1> transmigration across the BBB in the presence of anti-AnxA2 antibody compared to no antibody and mock antibody (P < 0.05, n = 8). (C) The integrity of the barrier was monitored by measuring FITC-dextran permeability across hBMECs (fluorescent intensity of the abluminal chambers/luminal chambers). The low permeability ratios confirmed that the barrier remained intact throughout the assays (P > 0.05, n = 8). *Indicates significant with P < 0.05.