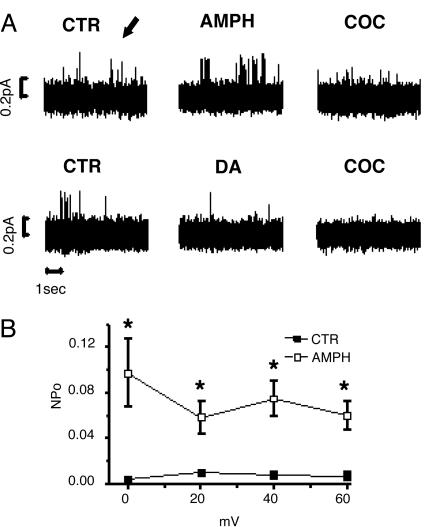
Fig. 2.
Substrate-regulated hDAT-mediated, outward channel-like activity. (A) Upper traces show sequential recordings of hDAT channel-like activity at +20 mV in control condition (CTR), after bath application of 10 μM AMPH (AMPH), and after bath application of 10 μM cocaine with AMPH still present (COC). Upward spikes signify outward channel-like current; see arrow. Lower traces show sequential recordings of hDAT channel-like activity at +20 mV in CTR, after bath application of 10 μM DA (DA), and after bath application of 10 μM cocaine with DA still present (COC). The fraction of the time that the hDAT channel is in the open state (NPo) and current (i) were calculated for each condition between 0 and 60 mV and reported in Fig. 2B and Fig. 6, which is published as supporting information on the PNAS web site. (B) The hDAT-channel NPo increases after AMPH application, compared with the CTR condition for each voltage tested (n = 4–6 for each voltage). *, significantly different from CTR, P < 0.05, paired t test.