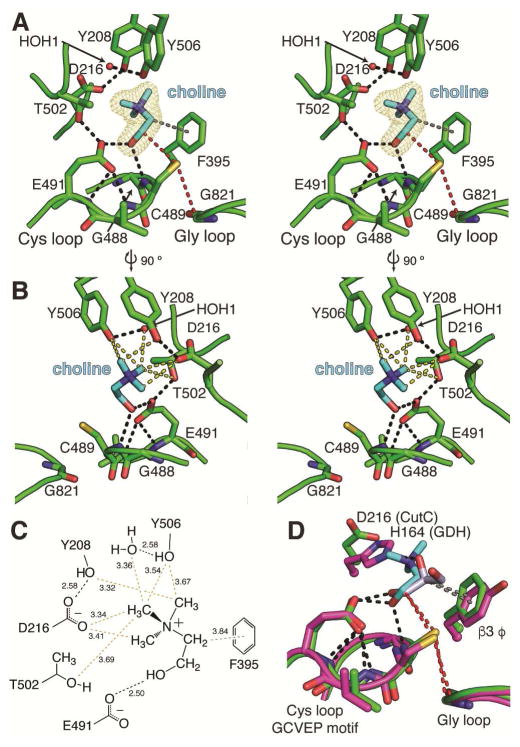
Figure 3. CutC binds substrate in a pocket above the Cys loop.
(A) Stereoimage of CutC bound to its substrate, choline (cyan). The proposed hydrogen atom transfer pathway from Gly821 to Cys489 to C1 of choline is marked (red dashes). Hydrogen bonds (2.5–3.2 Å) are shown for residues within the active site (black dashes). The average HO–C1–C2–N(Me3) dihedral angle is 61°. (B) Stereoimage of the CH---O hydrogen bonds (yellow dashes) present in the CutC-choline complex. (C) Diagram of protein and water interactions with the trimethylammonium moiety of choline with CH–O and hydrogen bond distances (Å). CH---O hydrogen bonds are indicated for C to O distances of 3.8 Å or less (yellow). Hydrogen bonds (black) and presumed cation-π interactions (gray) are shown between protein and substrate atoms. Distances (Å) are given in the diagram. The maximum-likelihood-estimated coordinate error is 0.20 Å. (D) Comparison of CutC (green) and GDH (magenta) active site residues involved in binding C1 and C2 (sticks). The Cys loop GCVEP motif is conserved between the two enzymes. An aromatic residue contributed from β3 coordinates C2 of choline (gray dashes). The proposed hydrogen transfer pathways (red dashes) between the active site Gly, Cys, and C1 are virtually identical in the two structures. See Figure S2 for sequence alignments and Figure S3 for additional CH---O hydrogen bonding analysis.