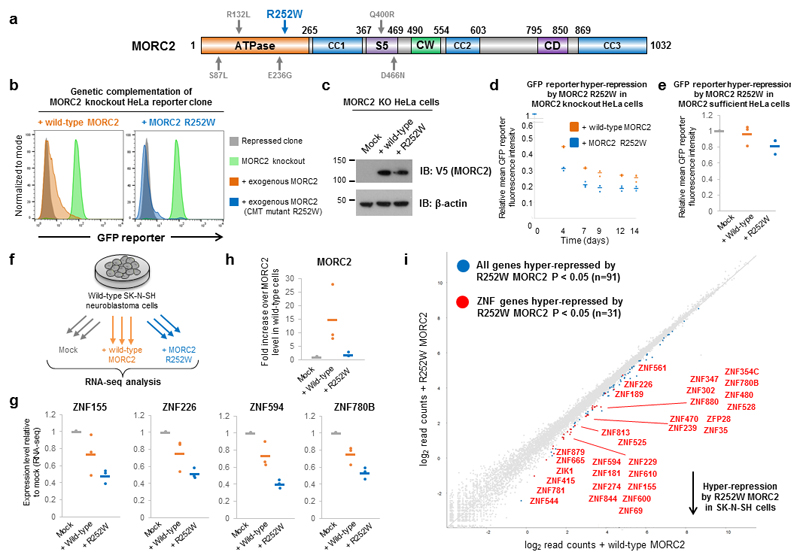
Figure 6. The R252W mutation in MORC2 associated with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease hyper-activates HUSH-mediated epigenetic repression.
(a) Schematic representation of the mutations associated with CMT affecting the ATPase domain of MORC2. (b,c) Assessing the effect of the R252W CMT mutation on MORC2 function through genetic complementation of MORC2 knockout cells. The R252W CMT mutant MORC2 is functional, restoring HUSH-mediated transgene silencing when expressed in MORC2 knockout cells (b). Immunoblot validation of expression of wild-type or R252W mutant MORC2 (c). (d,e) The R252W CMT mutation in MORC2 hyper-activates HUSH-mediated transgene silencing in HeLa cells. Time-course of transgene re-repression in MORC2 knockout HeLa cells (d): the R252W MORC2 mutant increases both the rate and overall extent of transgene re-repression. Hyper-repression of a GFPdim HUSH reporter in MORC2-sufficient cells by over-expression of R252W MORC2 (e). (f) Schematic representation of the RNA-seq experiment in wild-type SK-N-SH neuroblastoma cells. (g – i) Expression of either wild-type MORC2 or the R252W mutant results in hyper-repression of HUSH target genes. RNA-seq in SK-N-SH cells overexpressing either wild-type or R252W MORC2 reveals hyper-repression of example HUSH target genes (g); despite R252W MORC2 being expressed at a much lower level than the wild-type protein (h), this effect was more pronounced with the R252W mutant. In total, 91 genes were hyper-repressed by the R252W mutant (edgeR P < 0.05), of which 31 were ZNF genes (i).