FIG.1.
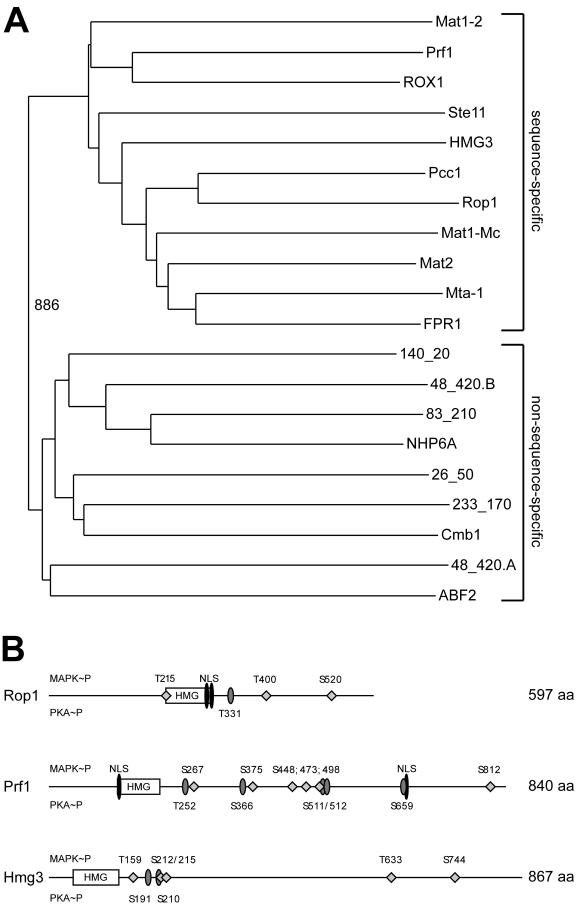
U. maydis genome contains three sequence-specific HMG domain proteins. (A) Bootstrap analysis (with Clustal X [48] and neighbor-joining plot programs) of the nine HMG domains encoded by the U. maydis genome compared to sequence-specific and non-sequence-specific HMG domains of several fungal species. Amino acid positions in the proteins are given as lowercase numbers. ABF243-111 (S. cerevisiae, accession no. sp|Q02486), Cmb1141-220 (S. pombe, accession no. sp|Q10241), NHP6A21-89 (S. cerevisiae, accession no. sp|P11632), FPR1169-237 (Podospora anserina, accession no. sp|P35693) Mta-1116-184 (Neurospora crassa, accession no. sp|P36981), Mat2 (Gibberella fujikuroi; accession no. dbj|BAA75905.1), Mat1-Mc103-171 (S. pombe, accession no. sp|P10840), Pcc124-98 (C. cinereus, dbj BAA33018.1), Ste1116-80 (S. pombe, accession no. sp|P36631), ROX110-83 (S. cerevisiae, accession no. sp|P25042), and Mat1-2129-203 (C. heterostrophus, accession no. pir|S34811). The HMG domains of Prf1126-197 (accession no. gb|AAC32736), Rop1215-295 (accession no. gb|AY677184), and Hmg357-140 (accession no. gb|AY677183) cluster with the sequence-specific class, whereas the other six Ustilago HMG domains given as annotation codes (http://mips.gsf.de/genre/proj/ustilago) appear in the non-sequence-specific class. (B) Schematic representation of U. maydis Rop1, Prf1, and Hmg3 domain structure. Features were identified with the PrositeScan and PSORT engines. Putative MAP kinase (diamonds) and protein kinase A (grey ellipses) phosphorylation sites are shown; numbers above the line indicate MAP kinase phosphorylation sites, and numbers below protein kinase A phosphorylation sites. The HMG domains are represented by open rectangles, and the potential nuclear localization sequences (NLS) are depicted as black ellipsoids. The numbers on the right indicate the sizes of the proteins in amino acids.