Figure 4. Rspo2+ and Ppp1r1b+ BLA neurons participate in valence-specific behaviors.
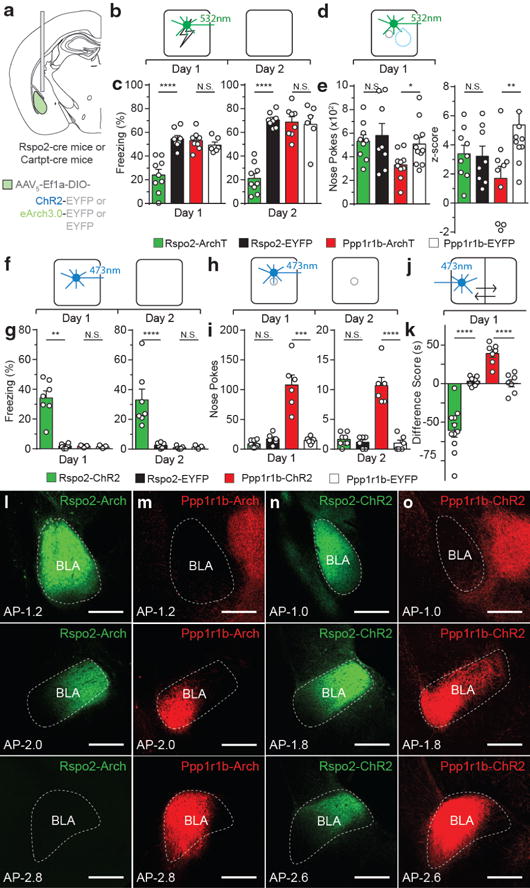
a, Optogenetically targeting Rspo2+ and Ppp1r1b+ BLA neurons. Scheme and results for Rspo2-Arch and Ppp1r1b-Arch mice in a fear (b,c) and reward (d,e) conditioning. c, Rspo2-Arch mice (n = 9) displayed lower freezing on Day 1 and 2 compared to eYFP controls (n = 8), no difference between Ppp1r1b-Arch (n = 8) and Ppp1r1b-eYFP (n = 6) mice. e, Ppp1r1b-Arch mice (n = 10) displayed lower total nose pokes and cue-reward association in nose port (z-score) compared to eYFP controls (n = 11), no difference between Rspo2-Arch (n = 9) and Rspo2-eYFP (n = 8). Scheme and results for Rspo2-ChR2 and Ppp1r1b-ChR2 mice in an optogenetic freezing test (f,g), optogenetic self-stimulation test (h,i), and optogenetic place preference test (j,k). g, Rspo2-ChR2 mice (n = 7) displayed greater freezing levels on Day 1 and 2 compared to eYFP controls (n = 6), no difference between Ppp1r1b-ChR2 (n = 5) and Ppp1r1b-eYFP (n =5) mice. i, Ppp1r1b-ChR2 mice (n = 6) displayed greater levels of nose pokes on day 1 and 2 compared to EYFP controls (n = 6), no difference between Rspo2-ChR2 (n = 8) and Rspo2-eYFP (n = 6) mice. k, Rspo2-ChR2 mice (n = 11) displayed greater preference to light stimulation compared to eYFP controls (n = 8), while Ppp1r1b-ChR2 (n = 7) mice displayed greater preference to light stimulation compared to eYFP controls (n = 7). Significance for unpaired t-test between experimental groups compared to corresponding eYFP controls, *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01, ***P<0 .001, ****P<00001, not significant (N.S), results show mean ± s.e.m (c,e,g,i,k). Expression of eArch-EYFP in Rspo2-Arch mice (l) and Ppp1r1b-Arch mice (m). Expression of ChR2-EYFPin Rspo2-ChR2 mice (n) and Ppp1r1b-ChR2 mice (o). Strong Ppp1r1b+ fibers are found in the central amygdala (m,o). Scale bar, 300μm (l,m,n,o). Color scheme corresponds to the virus-infected transgenic mouse, Rpso2-Cre (green) and Cartpt-Cre (red) (c,e,g,i,k,l–o).
