Figure 1. Placenta transcriptome.
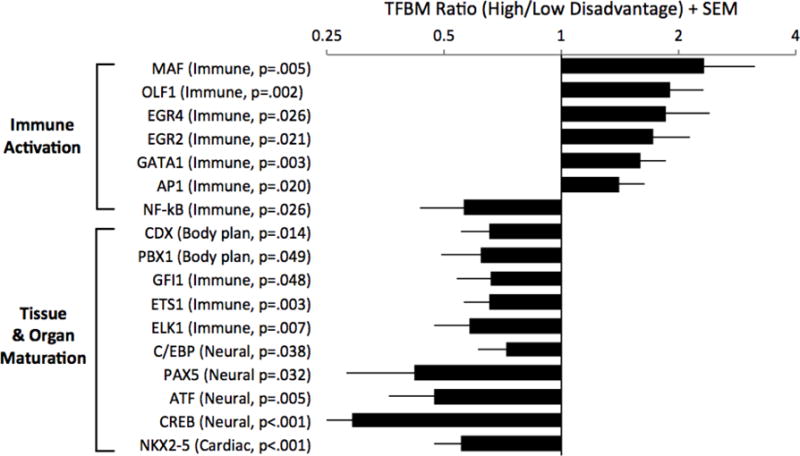
Genome-wide expression profiling was performed on biopsies of placental chorionic villi. Linear mixed models were used to estimate the magnitude of differential gene expression as a function of maternal socioeconomic disadvantage, adjusting for a panel of a priori selected covariates, with false discovery rate held at 5 percent. Genes showing ≥ 1.25-fold differential expression over the range from lowest to highest disadvantage served as input into higher-order bioinformatics analyses using the Transcription Factor Element Listening System. This platform quantified the prevalence of transcription factor binding motifs (TFBMs) in promoters of differentially expressed genes. TFBM ratios > 1 indicate specified transcriptional pathway is up-regulated with maternal disadvantage; ratios < 1 indicate converse.
