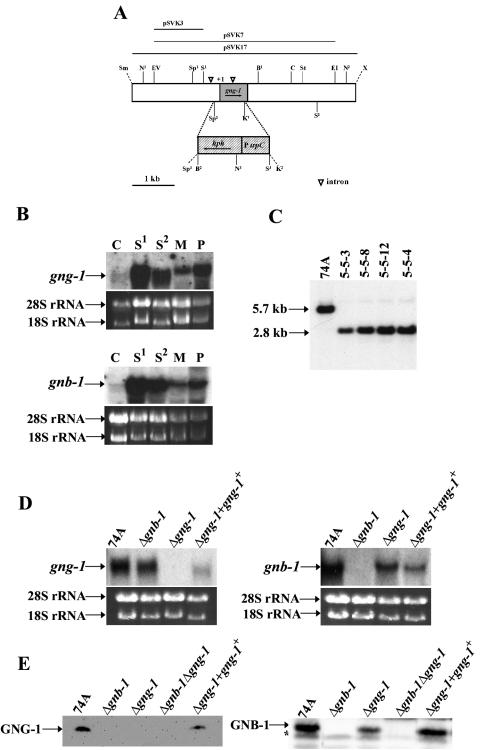
FIG. 2.
Structure of the N. crassa gng-1 genomic region and construction of Δgng-1- and Δgng-1 gng-1+-rescued strains. (A) gng-1 genomic clone and gene replacement vector. The grey area indicates the gng-1 ORF, and the hatched region corresponds to the gene conferring hygromycin resistance, hph, under control of the A. nidulans trpC promoter. The dashed lines illustrate the region replaced by hph that is between the second SpeI and first KpnI sites. The open triangles indicate intron positions (−511 to −197; +162 to +258). The arrows show the direction of transcription of gng-1 and hph. Abbreviations for restriction sites: N, NcoI; EV, EcoRV; Sp, SpeI; S, SalI; K, KpnI; B, BamHI; C, ClaI; St, StuI; E, EcoRI; X, XbaI; Sm, SmaI. KpnI2, SpeI3, and the unique XbaI and SmaI are artifacts of cloning. pSVK3 was the probe used for Southern analysis (see the legend to panel B). pSVK7 was used as the gene replacement construct, while the portion of gng-1 in pSVK17 was present in the his-3-targeted rescue construct. (B) Expression of gng-1 and gnb-1 during the N. crassa life cycle. Samples from wild-type strain 74A tissues (20 μg of total RNA) were subjected to Northern analysis using as probes a 1,074-bp PCR product amplified from pBR2 for detection of the gnb-1 transcript and a 279-bp PCR product amplified from pSVK1 to detect the gng-1 ORF. The tissues used in the experiment were as indicated. C,conidia; S1, 8-h submerged cultures; S2, 16-h submerged cultures; M, cultures grown for 3 days at 30°C on solid VM in the dark; P, cultures grown for 6 days at 25°C on SCM under light. Amounts of the major RNA species are shown as loading controls. (C) Southern analysis. Genomic DNA was digested with NcoI, and the 1.8-kb SalI-EcoRV fragment from pSVK3 was used as a probe. Strains 5-5-3, 5-5-8, and 5-5-12 are purified homokaryotic Δgng-1 mutants. Strain 5-4 is a Δgnb-1 Δgng-1 double mutant. (D) Northern analysis of mutant and wild-type strains. Samples containing 20 μg of total RNA isolated from 16-h submerged cultures were subjected to Northern analysis using a 1,074-bp PCR product amplified from pBR2 to detect the gnb-1 transcript and a 279-bp PCR product amplified from pSVK1 to detect gng-1 mRNA. The strains used in the analysis are 74A (wild type), Δgng-1 (5-5-12), Δgnb-1 (42-8-3), and Δgng-1 + gng-1+ 113-1. rRNA loading controls are as in panel B. (E) GNG-1 and GNB-1 protein levels in the wild type and mutants. Samples containing 30 μg of protein from plasma membrane fractions of 16-h submerged cultures were subjected to Western analysis using the GNG-1 and GNB-1 antibodies. The strains used in the analysis were 74A (wild type), Δgng-1 (5-5-12), Δgnb-1 (42-8-3), Δgnb-1 Δgng-1 5-4, and Δgng-1 + gng-1+ 113-1. The asterisk indicates a nonspecific band in the GNB-1 Western blot.