Figure 5. myrf-1 and myrf-2 cooperatively controls DD rewiring.
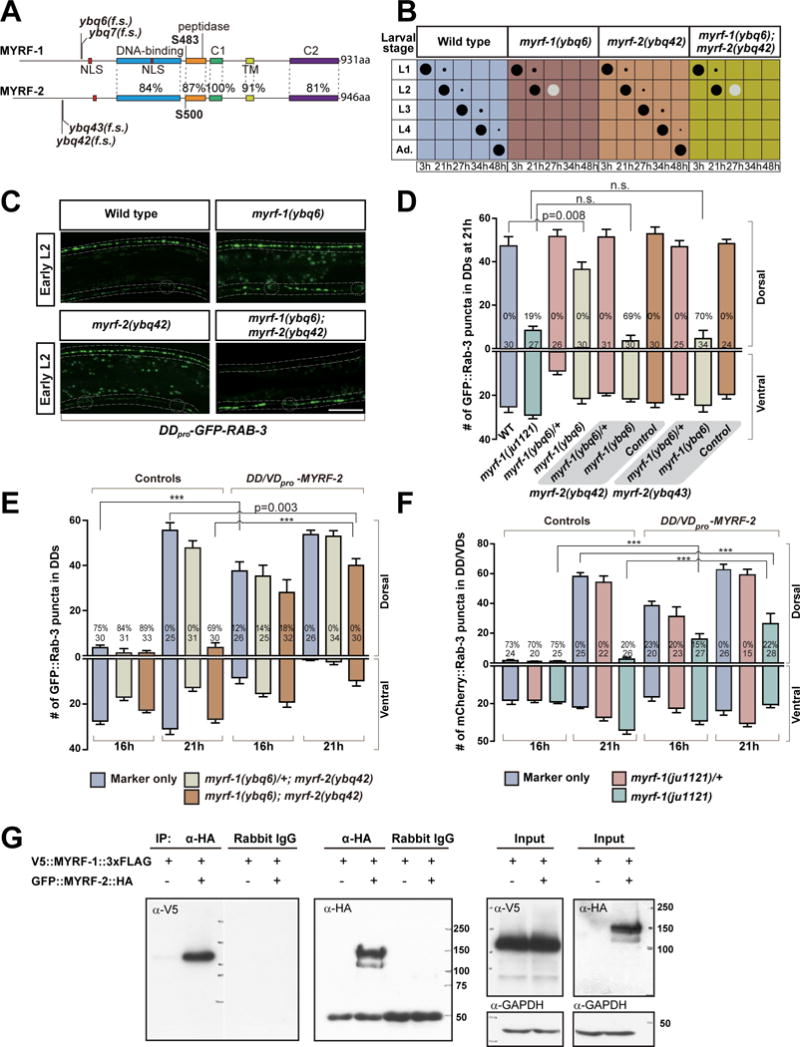
A. Comparison shows protein sequence and domain similarity between MYRF-1 and MYRF-2 (isoform c). Cleavage sites, S483 in MYRF-1 and S500 in MYRF-2, are conserved. The indel mutations cause frame shift (f.s.).
B. Assessment of larval development for myrf-1 and myrf-2 mutants. Size of black dots corresponds to percentage of the animals at specific larval stage. Light color dots represents arrested animals. n=300.
C. DD rewiring in myrf-1(ybq6), myrf-2(ybq42), and myrf-1(ybq6); myrf-2(ybq42) double mutants, labeled by flp-13pro-GFP∷RAB-3 (ybqIs47). Note the lack of dorsal synapses in double mutant. Dotted lines, ventral and dorsal cords; Dotted circles, DD neuron soma. Scale, 10 μm.
D. Number of synapses in myrf-1 and myrf-2 mutants labeled by flp-13pro-GFP∷RAB-3 (ybqIs47) is shown as mean ± SEM; t-test; the number of animals analyzed is shown on each bar. %, penetrance for animals with no dorsal synapse.
E. Number of synapses in animals over-expressing unc-25pro-myrf-2 (ybqEx529) labeled by flp-13pro-GFP∷RAB-3 (ybqIs47) is shown as mean ± SEM; t-test (***P<0.001); the number of animals analyzed is shown on each bar. %, penetrance for animals with no dorsal synapse. myrf-2 transgene rescues blocked DD rewiring in myrf-1; myrf-2 double mutants, and caused precocious DD rewiring at 16h.
F. Number of synapses in animals over-expressing unc-25pro-myrf-2 (ybqEx528) labeled by unc-25pro-mCherry∷RAB-3 (juIs236) is shown as mean ± SEM; t-test (***P<0.001); the number of animals analyzed is shown on each bar. %, penetrance for animals with no dorsal synapse. myrf-2 transgene partially suppresses the blocked rewiring in myrf-1(ju1121) mutant.
G. Co-immunoprecipitation of V5∷MYRF-1∷3xFlag and GFP∷MYRF-2∷HA, expressed in HEK293 cells.
